AI Summary
GIFT City in India is emerging as a prominent hub for Global and Regional Treasury Centers (GRCTCs), offering multinational corporations a strategic location to centralize financial operations. Regulated by the IFSCA, GIFT City provides a unified regulatory environment and attractive tax incentives, including exemptions and reduced dividend tax rates. GRCTCs in GIFT City facilitate efficient cash and liquidity management, FX risk hedging, and in-house banking services for group entities. The city's cost-effectiveness, skilled workforce, and strategic location as a gateway to Asia, the Middle East, and Africa make it a compelling alternative to traditional financial hubs. The regulatory framework supports various treasury activities, including cash pooling, intercompany lending, and commodity trading. With ongoing developments such as streamlined compliance and updated guidelines, GIFT City is set to become a key player in global financial services.
Last Updated on: 30th October 2025, 02:23 pm
Contents
- 1 Why GIFT City Treasury is Growing
- 2 What is a Global Treasury Centre (GTC)?
- 3 What is a Regional Treasury Centre (RTC)?
- 4 Regulatory Framework for Treasury Centres in GIFT City
- 4.1 What Are the IFSCA Finance Company Regulations, 2021?
- 4.2 GRCTCs: A Permitted Core Activity Under IFSCA
- 4.3 Who Can Set Up a GRCTC?
- 4.4 Structural Options for a GRCTC in IFSC
- 4.5 Timeline: Key Regulatory Milestones for GRCTC
- 4.5.1 June 2021: IFSC Committee Recommends GRCTC Focus
- 4.5.2 25 June 2021: GRCTC Framework Officially Launched
- 4.5.3 August 2021: Corporate Governance & Disclosure Guidelines
- 4.5.4 July 2022: Regulatory Relaxation for GRCTCs
- 4.5.5 March 2023: Concessional 10% Dividend Tax Introduced
- 4.5.6 October 2023: Compliance Simplification for Fund Transfers
- 4.5.7 September 2024: GRCTC Framework Review Initiated
- 4.5.8 April 2025: Revised GRCTC Framework Issued
- 4.5.9 Re-invoicing Model Approved (April 2025)
- 4.6 Hedging Rules Updated
- 5 Entity Structure Options for Setting Up a GRCTC in GIFT City
- 6 Why GIFT City for Global/Regional Treasury Centres?
- 6.1 1. India’s Regulatory Vision for Global Treasury Operations
- 6.2 2. Commercial Benefits of Centralized Pooling
- 6.3 3. Explicit GRCTC Benefits in GIFT IFSC
- 6.4 4. Tax Incentives & Fiscal Benefits for IFSC Treasuries
- 6.5 5. GST and Indirect Tax Breaks
- 6.6 6. Cost Advantage & Operational Efficiency
- 6.7 7. Talent Pool – Skilled Finance, Treasury & Legal Professionals
- 6.8 8. Strategic Location – Gateway to Asia, Middle East & Africa
- 6.9 9. Trade Credit & Insurance Ecosystem
- 6.10 Why Corporates Prefer GIFT IFSC for Treasury Centres
- 7 Treasury Activities Allowed in GIFT IFSC
- 8 Common GRCTC Structures in GIFT City
- 9 Setting Up a Treasury in GIFT IFSC (GRCTC): Complete Step-by-Step Guide
- 9.1 The Compliant Order: Register First, Operate Next
- 9.2 Step-by-Step Process for Setting Up a Treasury in GIFT IFSC
- 9.2.1 Step 1: Define your GRCTC model
- 9.2.2 Step 2: Secure space & prepare for SEZ application
- 9.2.3 Step 3: File IFSCA application for GRCTC on SWIT
- 9.2.4 Step 4: Meet entry conditions (prepare in parallel)
- 9.2.5 Step 5: Respond to queries & obtain registration
- 9.2.6 Step 6: Operationalize banking & currency rails
- 9.2.7 Step 7: Finalize policies, limits & controls
- 9.2.8 Step 8: Go-live & ongoing obligations
- 9.3 Practical Timeline (Indicative)
- 10 Exchange Control Guidelines for GRCTCs in GIFT City
- 11 Scope of Service: GRCTCs Can Serve Group Entities Only
- 12 Currency Rules for GRCTCs in GIFT City: What’s Allowed and What’s Not
- 13 Accounting, Reporting and Prudential Requirements for GRCTCs in GIFT City
- 14 Advanced Cash Pooling Structures in GIFT IFSC
- 15 GRCTCs as Commodity Trading and Hedging Hubs
- 16 Industry Use Cases & Case Studies
- 17 Challenges & Considerations for GTC/RTC in GIFT City
- 18 Future of GTC & RTC in GIFT IFSC
Why GIFT City Treasury is Growing
GIFT IFSC – India’s International Financial Hub
The Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City) was launched as India’s first International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) to attract global capital and consolidate offshore activities back into India. It operates as a greenfield smart city spread across 886 acres, divided into a Special Economic Zone (SEZ) and Domestic Tariff Area (DTA). The IFSC is regulated by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA), which consolidates powers of RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA to provide a single-window unified regulator.
Key highlights of GIFT IFSC include:
- 930+ entities registered, including global banks, insurers, and capital market players (as of June 2025).
- USD 93 billion+ total banking asset size.
- Tax benefits: 100% exemption for 10 out of 15 years, no GST on offshore transactions, 10% dividend tax for non-residents.
- Global-standard infrastructure: automated cooling and waste systems, underground utility tunnels, walk-to-work ecosystem.
Treasury Centres in GIFT City
Treasury Centres in GIFT City, operating within India’s International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), are specialized units either Global Treasury Centres (GTCs) or Regional Treasury Centres (RTCs) that act as the in-house bank for multinational corporations. Regulated by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA), they centralize and manage group-wide financial operations, focusing on multi-currency liquidity and cash management, foreign exchange and interest rate hedging, and intra-group financing. GRCTC refers to a Global or Regional Corporate Treasury Centre set up within India’s International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) at Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City). Governed by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA), these centers function as in-house banks for multinational corporations (MNCs) to manage global financial activities from a centralized hub.
A Global Treasury Centre (GTC) serves as the financial nerve center for a multinational group, consolidating global treasury functions to drive efficiency and control. Its key roles include liquidity and cash pooling across subsidiaries, FX and interest rate risk management, intra-group lending, and global capital deployment through instruments like bonds and external borrowings.
A Regional Treasury Centre (RTC) operates as the treasury hub for a defined geography such as Asia-Pacific or the Middle East. While a GTC manages global flows, an RTC supports regional subsidiaries by providing liquidity, FX hedging, and regulatory-aligned risk management. It bridges local operations and global headquarters, ensuring treasury alignment with both group strategy and regional market dynamics.
Why MNCs are Consolidating Treasury Operations
Global companies increasingly prefer centralized treasury centres for efficiency, compliance, and cost control:
- Operational efficiency: Central hubs reduce duplication of treasury functions across countries.
- Lower costs: GIFT City offers cost advantages vs hubs like Singapore or Dubai.
- Regulatory ease: One unified regulator (IFSCA) simplifies cross-border approvals.
- Tax savings: GTC/RTC in GIFT IFSC can benefit from tax neutrality on interest, dividend, and capital gains.
- Technology adoption: Treasury Management Systems (TMS), multi-currency pooling, and AI-driven risk analytics enhance real-time cash visibility.
Stat Snapshot – Why Treasury is Centralizing in GIFT City
| Factor | GIFT IFSC Advantage |
| Banking Assets | USD 93 bn+ (June 2025) |
| Entities Registered | 930+ (June 2025) |
| Tax Incentive | 100% exemption (10/15 yrs) |
| Dividend Tax | 10% for non-residents |
| Regulator | Unified IFSCA |
What is a Global Treasury Centre (GTC)?
A Global Treasury Centre (GTC) is the nerve centre of financial operations for multinational corporations (MNCs). It acts as an in-house bank for the group, consolidating financial decision-making, ensuring efficient use of capital, and enabling greater control over risks and liquidity across multiple geographies.
Core Functions of a Global Treasury Centre
A GTC typically undertakes the following critical activities:
- Cash & Liquidity Management
- Centralized pooling of cash across global subsidiaries.
- Optimization through notional pooling or physical cash concentration.
- Ensures funds are available where required, reducing idle balances.
- Risk Management
- Foreign exchange (FX) hedging to manage currency exposures.
- Interest rate risk mitigation through swaps, futures, and options.
- Commodity price hedging for corporates dealing with raw materials (e.g., oil, metals).
- In-House Banking
- Acting as a bank for group entities: providing intercompany loans, deposits, and settlements.
- Enabling netting of intra-group transactions, lowering transaction costs.
- Managing centralized payment and collection systems (“payment factory” model).
- Funding and Capital Allocation
- Raising debt or equity globally at competitive rates.
- Allocating capital efficiently across subsidiaries.
- Supporting external borrowings, ECBs, and bond issuances from one hub.
Global Examples of Treasury Hubs
Several established international hubs showcase the importance of GTCs:
- Singapore – Asia’s largest FX trading centre, third globally after London and New York; key hub for MNC treasury operations.
- Dublin (Ireland) – Favoured in Europe for tax treaties, access to EU markets, and robust regulatory frameworks.
- Hong Kong – Long-standing treasury hub for North Asia with free capital movement and proximity to China.
What is a Regional Treasury Centre (RTC)?
A Regional Treasury Centre (RTC) is a treasury hub that manages financial operations within a defined geographic region for example, Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, or Africa. Unlike a Global Treasury Centre (GTC), which oversees worldwide operations, an RTC focuses on regional subsidiaries, ensuring that local business needs are met while still aligning with the company’s global financial strategy.
RTC vs GTC: Key Differences
Comparing Regional Treasury Centre (RTC) and Global Treasury Centre (GTC)
| Feature | Regional Treasury Centre (RTC) | Global Treasury Centre (GTC) |
| Scope | Limited to a region (e.g., Asia, MEA) | Covers all global subsidiaries |
| Focus | Regional liquidity, FX risk, local compliance | Global capital allocation, worldwide liquidity & risk |
| Decision-making | Semi-centralized – aligns with global HQ but adapts to regional needs | Fully centralized – decisions flow from one global hub |
| Best for | Companies with strong presence in a particular region needing closer oversight | Companies aiming for complete centralization and efficiency |
How RTCs Serve Asia, Middle East, and Africa
RTCs are increasingly popular in emerging and frontier markets where business expansion is rapid but regulatory, FX, and banking environments vary by country.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC):
- Supports subsidiaries in India, Southeast Asia, and China.
- Provides FX hedging for volatile currencies and ensures liquidity across high-growth but fragmented markets.
- Middle East (ME):
- Manages funding and payments for oil & gas, infrastructure, and energy companies.
- Deals with currencies pegged to USD and regional banking regulations.
- Africa:
- Helps manage capital repatriation restrictions.
- Ensures availability of funds for operations in multiple currencies (e.g., ZAR, NGN, KES).
GIFT IFSC, strategically located in India, is increasingly positioned as a regional treasury hub for Asia, Middle East, and Africa, offering multi-currency pooling, zero-interest withholding tax, and tax holidays on treasury income.
Role in Bridging Global Operations with Regional Subsidiaries
RTCs play a critical bridge function between headquarters and local entities:
- Alignment with global treasury policies while adapting to regional regulations.
- Real-time liquidity management for subsidiaries across time zones.
- Consolidated reporting for regional entities before submission to global HQ.
- Support for local financing (e.g., trade finance, supply chain financing).
- Risk monitoring for region-specific exposures (political, currency, and commodity risks).
This layered structure ensures both control at the centre and agility in the region, making RTCs essential for companies with diverse regional operations.
When Do Companies Choose RTC Instead of GTC?
Companies often opt for a Regional Treasury Centre instead of a Global Treasury Centre in the following situations:
- Strong regional presence – Businesses with large revenues in Asia or Africa often need localized treasury oversight.
- Regulatory barriers – When certain jurisdictions restrict full centralization of treasury, RTCs offer a compliant alternative.
- Currency complexity – Emerging markets with volatile or restricted currencies require on-ground management.
- Stepping stone to global centralization – Many MNCs start with RTCs before consolidating into a GTC.
- Sector-specific needs – Industries like oil & gas, manufacturing, and IT services often use RTCs to optimize working capital in growth-heavy regions.
Regulatory Framework for Treasury Centres in GIFT City
What Are the IFSCA Finance Company Regulations, 2021?
The IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021, notified in March 2021 by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA), establish the legal foundation for non-banking financial activities within GIFT City’s International Financial Services Centre (IFSC).
These regulations enable global and Indian entities to operate finance companies or branches (called finance units) from GIFT IFSC under a unified, streamlined regime. The IFSCA consolidates regulatory authority from RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA, offering a single-window approval system for financial services in IFSCs.
GRCTCs: A Permitted Core Activity Under IFSCA
Operating a Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC) is explicitly listed as a core permissible activity for finance companies or finance units registered in GIFT IFSC.
- Permitted via a dedicated framework issued on 25 June 2021
- Detailed in Circular No. F. No. 331/IFSCA/GRCTC/2021-22
- Aimed at multinational corporations and Indian conglomerates seeking to centralize global treasury functions
- GRCTCs can provide both treasury activities (e.g., intra-group funding, FX transactions) and treasury services (e.g., cash pooling, risk management), exclusively for group entities
Who Can Set Up a GRCTC?
Any eligible entity may apply for registration under the IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021 to set up a GRCTC, subject to:
- Prior approval from IFSCA
- Compliance with eligibility norms (including group structure and jurisdictional vetting)
- Non-engagement with countries on the FATF high-risk list, unless specifically approved by the Indian government
Structural Options for a GRCTC in IFSC
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Finance Company (FC) | A separate legal entity (subsidiary, joint venture, or new entity) |
| Finance Unit (FU) | A branch of an existing Indian or foreign finance company |
Entities can choose the structure based on global treasury footprint, tax strategy, and compliance priorities.
Timeline: Key Regulatory Milestones for GRCTC
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| March 2021 | IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021 notified |
| June 2021 | GRCTC framework introduced via formal circular |
| August 2021 | Corporate governance and disclosure rules issued for finance companies |
| July 2022 | Prudential norms relaxed and capital requirements reduced for GRCTCs |
| March 2023 | 10% concessional dividend tax for non-resident shareholders introduced |
| Oct 2023 | Simplified 15CA/15CB filing for GIFT City remittances |
| Sept 2024 | IFSCA issued consultation paper to review and update GRCTC framework |
| April 2025 | Revised GRCTC framework issued, with clarified activity list and scope |
June 2021: IFSC Committee Recommends GRCTC Focus
In June 2021, an IFSCA-appointed advisory committee on offshore INR markets recognized GRCTCs as a strategic lever for boosting GIFT IFSC activity. The report:
- Advocated for GRCTC adoption by Indian multinationals
- Encouraged policy support for centralized global treasury functions
- Set the stage for the formal regulatory framework that followed
25 June 2021: GRCTC Framework Officially Launched
Following the committee’s recommendation, the IFSCA issued the Framework for undertaking Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre Activities by Finance Companies/Units on 25 June 2021.
Key Features
- GRCTC permitted for both Finance Companies (FCs) and Finance Units (FUs)
- Treasury services restricted to eligible group entities in FATF-compliant jurisdictions
- Enables use of IFSC as an in-house treasury bank for global cash, risk, and investment operations
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Effective Date | 25 June 2021 |
| Eligible Entities | FCs and FUs registered under the 2021 Regulations |
| Client Scope | Group entities only (subsidiaries, branches, JVs, etc.) |
| Key Activities | FX, intra-group lending, cash pooling, re-invoicing, corporate finance |
August 2021: Corporate Governance & Disclosure Guidelines
To align with international standards, IFSCA released mandatory Corporate Governance and Disclosure Requirements for all IFSC finance companies in August 2021.
Highlights
- Mandatory Board-approved policies for risk, governance, AML, and operations
- Ongoing disclosure of financials and compliance
- Applies to both new and existing treasury units
July 2022: Regulatory Relaxation for GRCTCs
IFSCA released a circular offering regulatory relief to GRCTCs, including:
- Exemption from standard prudential norms (capital adequacy, liquidity coverage, exposure limits)
- Minimum capital reduced to USD 0.2 million
These changes encourage faster onboarding and broader adoption of GIFT IFSC for treasury operations.
March 2023: Concessional 10% Dividend Tax Introduced
The Finance Act 2023 implemented a 10% flat tax rate on dividends distributed by GIFT IFSC units to non-resident shareholders—a major incentive compared to domestic dividend taxation.
| Shareholder Type | Dividend Tax Rate (Post-2023) |
|---|---|
| Non-resident (IFSC-based) | 10% |
| Domestic (India-based) | Higher slab rates |
October 2023: Compliance Simplification for Fund Transfers
IFSCA and MoF streamlined remittance procedures:
- Form 15CA removed for most IFSC outward remittances
- Form 15CB/CD requirements simplified and made quarterly
This update reduces compliance friction and eases operational transactions.
September 2024: GRCTC Framework Review Initiated
IFSCA released a public consultation paper to gather feedback on:
- Permitted GRCTC activities
- Currency and compliance limits
- Capital thresholds and onboarding timelines
This move reflects IFSCA’s intent to keep the framework adaptive and globally competitive.
April 2025: Revised GRCTC Framework Issued
Based on industry feedback, IFSCA issued updated guidelines for GRCTCs on 4 April 2025 to enhance clarity, usability, and market alignment.
Key Clarifications
- Expanded treasury service definitions (hedging, re-invoicing, guarantees)
- Simplified structural eligibility for Finance Units and Companies
- Faster approval mechanisms for group entity lists and business plan updates
Re-invoicing Model Approved (April 2025)
The revised framework explicitly allows GRCTCs to operate re-invoicing models under a Bill-to-Ship-to structure:
- GRCTC finances and invoices the transaction
- Goods ship directly to the end-customer
- All documentation must comply with trade and customs laws
This enables effective FX control and liquidity centralization for trading multinationals.
Hedging Rules Updated
GRCTCs may now:
- Enter OTC derivative contracts with both internal and external counterparties
- Hedge currency, interest rate, and commodity exposures
However, industry observers note that comprehensive guidelines for commodity hedging, especially for exchange-traded contracts, are still awaited.
Entity Structure Options for Setting Up a GRCTC in GIFT City
One of the most important regulatory flexibilities offered by the IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021 is the ability to choose between two distinct legal structures when setting up a Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC) in GIFT IFSC.
This structural clarity is vital for global corporations and Indian conglomerates evaluating tax, compliance, and capital strategy.
What Are the Two GRCTC Structures?
GIFT City allows treasury centres to be established in either of the following ways:
| Structure Type | Description | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Finance Company (FC) | A newly incorporated legal entity in GIFT IFSC. Can be a subsidiary or joint venture (JV) of a domestic or foreign parent. | Large multinationals needing full operational autonomy and dedicated capital deployment |
| Finance Unit (FU) | A branch of an existing foreign finance company, operating under IFSC license. | Global corporations seeking faster entry and leveraging existing infrastructure |
The minimum capital (owned funds) needed for a Finance Company/Unit conducting treasury centre activities in GIFT IFSC is only USD 0.2 million, compared to the USD 3 million normally required for other finance companies
Both structures are permitted to undertake GRCTC activities, subject to registration and regulatory compliance with IFSCA.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Finance Company (FC) | Finance Unit (FU) |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Identity | Separate entity (subsidiary/JV) | Extension of existing foreign company |
| Capital Requirement | As prescribed (e.g., USD 0.2 million for GRCTC) | Generally same, but lower entry barriers possible |
| Setup Speed | Requires incorporation, longer onboarding | Faster due to branch model |
| Control & Autonomy | Full operational independence | Linked to parent operations |
| Compliance Burden | Independent regulatory and tax filings | Consolidated compliance under parent entity |
Why GIFT City for Global/Regional Treasury Centres?
Following are the Key Advantages of Setting up a Treasury Centre in GIFT City
1. India’s Regulatory Vision for Global Treasury Operations
The Government of India, through the Ministry of Finance (MoF), the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA), has positioned GIFT IFSC as a leading destination for establishing Global and Regional Treasury Centres (GTCs/RTCs).
- IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021: Enabled finance companies and units in GIFT City to undertake treasury functions such as intra-group financing, liquidity management, and risk management.
- GRCTC Framework (June 2021): Permits finance companies and finance units to act as GTCs/RTCs, offering cash pooling, capital allocation, hedging, and risk mitigation for multinational groups.
- 2023–25 regulatory updates: Introduced multi-currency pooling, clarity on re-invoicing, OTC derivative participation, and permissions for holding company activities, mirroring the sophistication of Singapore and Dublin.
- Unified Oversight under IFSCA: Consolidates powers of RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA, creating a single-window regulatory structure that simplifies compliance for cross-border treasury operations.
2. Commercial Benefits of Centralized Pooling
Corporates and competitors highlight the tangible operational advantages of locating their treasury in GIFT IFSC:
- Consolidated fund management across subsidiaries and jurisdictions.
- Higher utilization of surplus cash and improved intra-group liquidity.
- Ability to pool and invest in foreign currency, enhancing returns and flexibility.
- Access to foreign exchange at competitive market rates.
- Group-wide cash visibility and centralized decision-making, leading to reduced idle balances and optimized capital deployment.
This centralization enables treasury teams to leverage technology-driven treasury management systems (TMS/CTRM) and gain real-time oversight across geographies.
3. Explicit GRCTC Benefits in GIFT IFSC
The GIFT IFSC GRCTC model offers comprehensive strategic and operational benefits:
- Cash netting and liquidity visibility across global subsidiaries.
- Tax incentives from both home and host jurisdictions.
- Proximity to financial markets and participants, enabling faster settlements.
- Efficient hedging and commodity trading opportunities through IFSC exchanges.
- Adoption of advanced treasury and risk management technologies (e.g., CTRM systems).
- Operational cost reduction via process centralization and automation.
These make GIFT City a robust alternative to Singapore, Dubai, and Hong Kong for treasury consolidation.
4. Tax Incentives & Fiscal Benefits for IFSC Treasuries
GIFT IFSC offers one of the most tax-efficient regimes globally:
- 100% income-tax exemption for any 10 consecutive years out of 15.
- MAT/AMT capped at 9%, and MAT not applicable if the company opts for the new concessional regime.
- 10% tax on dividends distributed by IFSC units to non-residents.
- Tax exemption on interest income paid by IFSC treasuries to non-resident group entities.
- Deemed-dividend provisions inapplicable where the IFSC unit’s parent is a foreign listed company.
- Stamp duty and capital gains relief, significantly lowering transaction costs.
Collectively, these provisions make IFSC-based treasuries cost- and tax-neutral for multinational groups managing global liquidity.
5. GST and Indirect Tax Breaks
In addition to direct tax incentives, GIFT IFSC units enjoy a favourable indirect tax regime:
- No GST on services rendered to offshore clients, IFSC units, or SEZ entities.
- No GST on input services received by IFSC treasury units.
- GST applies only on services provided to the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) or onshore India.
- State-level incentives such as subsidies and reduced registration fees further enhance cost efficiency.
This ensures near-total tax neutrality for international treasury operations conducted from GIFT City.
6. Cost Advantage & Operational Efficiency
GIFT City offers a 30–40% lower cost base than global treasury hubs:
- Reduced real estate, compliance, and workforce costs.
- Unified compliance under IFSCA reduces administrative burden.
- Access to world-class infrastructure comparable to Singapore and Hong Kong at a fraction of the cost.
7. Talent Pool – Skilled Finance, Treasury & Legal Professionals
India produces over 2.5 million commerce and finance graduates annually, supported by chartered accountants, CFAs, and treasury specialists.
This deep, cost-effective talent pool gives corporates a competitive edge in treasury operations, risk management, and cross-border finance.
8. Strategic Location – Gateway to Asia, Middle East & Africa
GIFT City’s time zone offers natural synergy with major markets:
- Overlap with Asia, Middle East, and Europe business hours.
- Regional coverage across APAC, MENA, and Africa.
- Proximity to India’s USD 3.94 trillion economy, expected to exceed USD 5 trillion by FY 2030, connects treasuries directly to the world’s fastest-growing demand hub.
9. Trade Credit & Insurance Ecosystem
The IFSC ecosystem is expanding to include trade credit and freight insurance players, crucial for corporate treasury efficiency:
- Enables supply chain financing and factoring at competitive rates.
- Provides risk cover and insurance benefits leveraging IFSC’s tax regime.
- Strengthens India’s trade finance backbone, allowing treasuries to integrate insurance and liquidity seamlessly.
Key Benefits of GTC/RTC in GIFT City vs Other Global Hubs
| Factor | GIFT City (India) | Singapore | Dubai | Hong Kong |
| Tax Regime | 100% exemption for 10/15 yrs; 10% dividend tax; interest income exempt | 17% corporate tax (effective Jan 2025); no WHT on dividends | 0% corporate tax (non-oil sectors), 5% VAT | 16.5% corporate tax; no WHT on dividends |
| FX Regulations | Full convertibility in 15 currencies; INR not permitted | Free capital convertibility | Free capital convertibility | Free capital convertibility |
| Cost of Operations | Lower office, compliance & workforce costs | High – among world’s costliest cities | Moderate; attractive incentives but rising costs | High – real estate & wage inflation |
| Capital Markets Access | Direct access to India’s $3.94T economy and growing debt & equity markets | Strong ASEAN market access | Middle East + Africa; limited Asia linkages | Access to China + global FX hub |
Why Corporates Prefer GIFT IFSC for Treasury Centres
- Regulatory clarity & global-standard compliance under IFSCA.
- Highly competitive tax regime driving cost savings.
- Proximity to India’s economy and regional trade flows.
- Cost arbitrage in workforce and infrastructure vs Singapore & Dubai.
- Government vision to make GIFT IFSC the “Global Nerve Centre of Financial Services” by 2047.
Treasury Activities Allowed in GIFT IFSC
The International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) at GIFT City allows multinational corporations to establish Global Treasury Centres (GTCs) and Regional Treasury Centres (RTCs) with a wide spectrum of treasury activities. These are enabled under the IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021 and the Framework for Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centres issued in June 2021. Here are activities what a GRCTC can do.
Centralized Cash Pooling & Liquidity Management
- Physical pooling: Sweeping funds from subsidiaries into a central account.
- Notional pooling: Virtual consolidation of balances in multiple currencies without physical transfers.
- Multi-currency cash pools allowed in GIFT City reduce FX conversion costs and optimize liquidity.
- Enables working capital efficiency across Asia, Middle East, and Africa.
- Supports daily fund sweeping into the IFSC treasury centre, subject to FEMA guidelines.
FX Risk Hedging & Derivatives
- Access to OTC derivatives and exchange-traded contracts.
- Permitted instruments: forwards, swaps, options, cross-currency derivatives.
- Corporates can hedge currency, interest rate, and commodity price risks.
- Regulatory updates (2023–25) allow greater participation in multi-leg and INR-linked contracts, provided one leg is in a freely convertible currency.
Investment of Surplus Funds
- Surplus funds can be invested in:
- Government securities
- Corporate bonds
- Money market instruments
- IFSCA permits foreign currency denominated investments, enabling higher yield versus local markets.
- Facilitates global liquidity optimization and better return on idle funds.
Fundraising – Loans, Bonds & ECBs
- Treasury centres in GIFT City can raise funds through:
- External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
- Bond issuances including green bonds and ESG-linked securities
- Syndicated loans and structured finance
- Advantage: Lower withholding tax, tax exemption on interest to non-residents, and easier access to India’s debt capital markets.
Intercompany Lending
- GRCTCs can provide intra-group loans across jurisdictions.
- Supports subsidiaries in managing liquidity gaps without relying on external borrowing.
- Loans structured with flexibility on maturity, currency, and interest rates.
- Helps reduce overall cost of capital for multinational groups.
In-House Banking Services
Treasury centres act as an “internal bank” for group entities. Services include:
- Payment factory: Centralized processing of vendor and supplier payments.
- Re-invoicing models: Enables risk-neutral billing and liquidity optimization across cross-border trade.
- Netting services: Offset receivables and payables within the group to minimize transaction volume and FX exposure.
- Virtual accounts: Enable internal settlements without physical movement of funds.
- Intercompany guarantees: Issuing credit support tools like guarantees and standby LCs.
- Banking and investor relations: Managing relationships with banks, lenders, and debt/equity investors.
- Treasury system integration: Operating or advising on Treasury Management Systems (TMS) and daily liquidity dashboards.
- Corporate finance support: Assisting group entities with budgeting, debt structuring, and capital raising.
- Compliance and controls: Supporting adherence to group treasury policies, accounting standards, and IFSCA regulations.
- Strategic research: Providing macroeconomic, liquidity, and investment insights to support business planning.
These services are allowed only for group entities (subsidiaries, branches, JVs, associates), subject to IFSCA rules. Entities in FATF high-risk jurisdictions are excluded unless expressly permitted by the Government of India.
Common GRCTC Structures in GIFT City
Setting up a Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC) in GIFT City allows multinational and Indian conglomerates to centralize cash, lending, FX, and investment operations efficiently. The IFSCA framework supports both Indian and foreign group structures through flexible finance company or branch models. Below are two common and regulator-recognized GRCTC structures:
1. Indian Parent Company with Foreign Subsidiaries
Use Case: An Indian-headquartered multinational creates a GRCTC in GIFT IFSC to pool and manage group liquidity and financing for its overseas subsidiaries.
Structure Overview:
- Indian parent sets up a Finance Company or Finance Unit in GIFT City
- Overseas group entities sweep excess funds or receive funding via the GRCTC
- GRCTC manages:
- Cash pooling
- Intra-group loans
- FX conversions
- Treasury investments
Key Benefits:
- Facilitates outbound financing at lower cost
- Enables access to foreign currency capital
- Reduces tax leakage through interest exemption on payments to non-residents
| Role | Entity Location |
|---|---|
| GRCTC | GIFT City IFSC |
| Parent Entity | India |
| Group Recipients | Overseas subsidiaries (non-FATF high-risk) |
2. Foreign Multinational with Indian Subsidiary
Use Case: A global corporation establishes a GIFT City GRCTC to manage funding for its Indian operations and regional expansion.
Structure Overview:
- Foreign parent company sets up a branch (Finance Unit) in GIFT IFSC
- The GRCTC receives capital or debt funding from the global parent
- Funds are lent to Indian subsidiaries for:
- Working capital
- Capex
- Trade finance
Key Benefits:
- Enables efficient inbound capital flow into India
- Minimizes currency and liquidity risks through centralized treasury control
- Gains from concessional tax regime and ECB flexibility
| Role | Entity Location |
|---|---|
| GRCTC | GIFT City IFSC |
| Parent Entity | Outside India |
| Group Recipients | Indian subsidiaries |
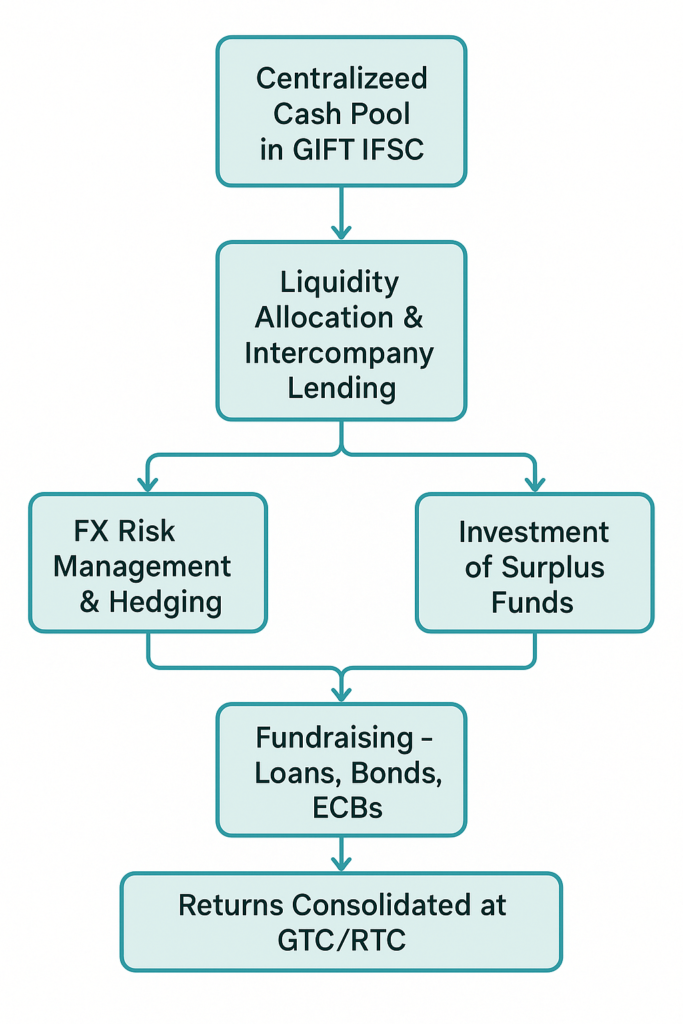

In the Image: Functional Structure of GIFT Treasury
Role of Technology in Corporate Treasury Services
- Digital Treasury Platforms enable 24/7 global visibility of liquidity and payments.
- AI/ML Risk Analytics help forecast FX exposure and liquidity shortages with higher accuracy.
- Automation reduces human error in intercompany transactions and derivatives execution.
- Blockchain & APIs enable instant settlements and faster reconciliation across multiple jurisdictions.
Integration with India’s Domestic and Cross-Border Capital Flows
- GIFT IFSC allows direct access to India’s growing equity, debt, and derivatives markets, providing corporates with funding options not available in other hubs.
- Seamless integration with onshore India entities ensures smoother ECB approvals, trade finance, and capital repatriation.
- Corporates can manage cross-border flows to Asia, Middle East, and Africa through a single treasury hub in India.
Setting Up a Treasury in GIFT IFSC (GRCTC): Complete Step-by-Step Guide
Thinking of centralizing group cash, FX, and intercompany funding in GIFT City IFSC? Under IFSCA’s Finance Company Regulations, 2021, you can establish a Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC) either as:
- An IFSC-incorporated Finance Company (FC) – such as a subsidiary or joint venture, or
- A Finance Unit (FU) – a branch of an Indian or overseas parent company.
This flexibility allows multinational groups and Indian conglomerates to choose the best-fit structure for tax, compliance, and operational alignment.
The Compliant Order: Register First, Operate Next
Yes, registration comes first. You must secure:
- GIFT-SEZ Unit Approval (Letter of Approval, “LOA”) from the Development Commissioner or IFSCA (as per delegated powers effective Feb 2024)
- IFSCA Certificate of Registration as a Finance Company or Finance Unit for GRCTC, filed on the SWIT portal (Single Window IT)
Only after both approvals are granted should you operationalize banking rails, FX/derivatives, and intercompany transactions.
Step-by-Step Process for Setting Up a Treasury in GIFT IFSC
Step 1: Define your GRCTC model
- Decide legal form: Finance Company (subsidiary/JV) or Finance Unit (branch) of the parent
- Scope the service recipients (must be group entities domiciled outside FATF high-risk jurisdictions, unless exempted by Indian government treaty/order)
- Map activity set: FX and derivatives, intercompany funding, re-invoicing, liquidity pools, investments
- Draft a concise business plan: use-cases, balance sheet size, risk appetite, technology stack
Step 2: Secure space & prepare for SEZ application
- Identify office space in GIFT-SEZ (lease/LoI)
- Prepare entity KYC, ownership structure, brief project report, and utility requirements
Target outcome: GIFT SEZ Letter of Approval (LOA) a prerequisite for the IFSCA application
Step 3: File IFSCA application for GRCTC on SWIT
- Create a SWIT account and file the GRCTC application under the Finance Company Regulations, 2021
- Attach supporting documents:
- Business plan
- Ownership and capital structure
- List of service recipient entities
- Draft internal policies:
- Governance
- Risk & Treasury Operations
- AML/CFT/KYC
- Activity scope & dealing limits
- Organizational chart with functional reporting lines
- Choose your structure:
- Finance Company (incorporated in IFSC)
- Finance Unit (branch of Indian or foreign company)
Step 4: Meet entry conditions (prepare in parallel)
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Owned Funds | Minimum USD 0.2 million for GRCTC (can be held at parent level if FU) |
| Staffing | At least 5 on-ground staff in IFSC, including Head of Treasury and Compliance Officer |
| Infrastructure | Treasury platforms, connectivity, information security, audit & monitoring |
Step 5: Respond to queries & obtain registration
- Address any clarifications or data requests from IFSCA
- Provisional approval may be issued first; final Certificate of Registration follows upon compliance
- Keep Service Recipient list updated during and after the application process
Step 6: Operationalize banking & currency rails
- Open operating accounts in freely convertible foreign currencies with IFSC banks
- For India-facing flows, open a Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account with an AD Cat-I bank
- Integrate treasury systems for trade booking, confirmations, settlements, reconciliation & MIS
Note: All treasury transactions must be in freely convertible currencies. INR is only allowed for administrative expenses via a separate rupee account.
Step 7: Finalize policies, limits & controls
- Obtain Board-approved policies covering:
- Corporate governance
- Risk management and dealing limits
- AML/CFT/KYC
- Business continuity (BCP/DR)
- Outsourcing controls
- Establish three lines of defense:
- Front office
- Risk/compliance
- Internal audit
- Define control metrics: counterparty limits, VaR/sensitivity checks, exception thresholds, daily/weekly reporting
These policies align with IFSCA’s August 2021 Corporate Governance and Disclosure Requirements.
Step 8: Go-live & ongoing obligations
- Commence operations within 6 months of IFSCA registration (seek extension if needed)
- Maintain:
- Minimum capital thresholds
- Required on-ground staffing
- Accurate books in freely convertible currency (maintain INR books for compliance)
- Timely submission of annual returns, compliance reports, and audited financials (in USD)
- Ensure activity scope and recipients stay aligned with approved GRCTC framework
Practical Timeline (Indicative)
| Phase | Timeline | Key Milestones |
|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1–3 | Pre-filing | Model definition, structure decision, policies, space & team |
| Weeks 4–10 | SEZ + IFSCA Filing | SEZ LOA, IFSCA GRCTC application, respond to clarifications |
| Weeks 8–14 | Operationalization | Staff onboarding, system testing, bank account setup |
| Month 3–4 | Go-Live | Policies finalized, registration in place, treasury live |
Exchange Control Guidelines for GRCTCs in GIFT City
Setting up a Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC) in GIFT City involves specific exchange control regulations governed primarily by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). These rules ensure proper oversight on cross-border capital flows and apply to Indian parent companies as well as GIFT-based treasury subsidiaries.
Funding the IFSC Treasury Unit from India: ODI Route
An Indian company can fund its GRCTC unit in GIFT City using the Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) route under India’s Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
Key Points:
- The GRCTC in GIFT City qualifies as a foreign entity under ODI norms (despite being in India), due to IFSC’s treatment as an external jurisdiction for FEMA purposes
- The investment must comply with the ODI Master Direction and updated FEMA circulars
Intent Clarified: Indian companies can treat capital infusion into GIFT IFSC treasury centres as an overseas investment.
Daily Fund Sweeping to GIFT IFSC
Indian group entities may sweep funds daily into their treasury centre at GIFT IFSC. However, such cash pooling and liquidity transfers are subject to:
- RBI’s exchange control framework
- Permitted transaction rules under FEMA
- Proper documentation of intra-group service relationships
While GIFT IFSC is outside India for FEMA, Indian entities remain residents and must comply with residence-based transfer pricing and forex limits.
External Commercial Borrowing (ECB) by IFSC Treasury Units
GIFT City treasury centres (GRCTCs) are eligible to raise External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) for the benefit of their group entities, subject to RBI guidelines.
Use Case:
- The GRCTC raises USD-denominated debt (via ECB) from foreign banks or investors
- The funds are then on-lent to group companies in India or abroad for working capital, capex, or refinancing
ECB Highlights for IFSC Units:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Eligible Borrowers | IFSC-registered Finance Companies or Finance Units |
| End-Use Flexibility | High — includes intra-group lending, debt repayment, liquidity support |
| RBI Compliance | Must comply with ECB Master Direction, all-in-cost ceilings, and reporting norms |
| Tax Advantage | Interest paid to non-resident lender is tax-exempt if routed via GIFT IFSC |
Scope of Service: GRCTCs Can Serve Group Entities Only
Under the IFSCA’s Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC) Framework, treasury centres set up in GIFT City IFSC are restricted to serving group entities only. This is a core regulatory condition, and understanding it is crucial for compliance, structuring, and eligibility.
Who Qualifies as a “Group Entity”?
According to the 25 June 2021 IFSCA GRCTC Framework, a group entity is defined comprehensively to allow flexibility while ensuring regulatory safeguards.
A group entity includes:
- Holding companies
- Subsidiaries
- Associate companies
- Joint ventures
- Branches
- Any entity that is part of the same corporate group structure
Legal Basis: Entities must be registered with a competent statutory body in their home jurisdiction to qualify.
Jurisdictional Restrictions: FATF Compliance Required
GRCTCs cannot offer treasury services to group entities that are:
- Domiciled in countries listed by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) as “High-Risk Jurisdictions Subject to a Call for Action”
- Unless specifically permitted by the Government of India through:
- A bilateral agreement or treaty, or
- A notification/order issued by competent authorities
This ensures alignment with India’s anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CFT) obligations.
Summary Table: Eligibility to Receive GRCTC Services
| Entity Type | Eligible? | Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Wholly-owned subsidiaries | ✅ | Must be registered in a FATF-compliant jurisdiction |
| Overseas branches of Indian firms | ✅ | Allowed if registered and within the group |
| Joint ventures with foreign firms | ✅ | Permitted under group entity definition |
| Unrelated third parties | ❌ | Not permitted |
| Entities in FATF high-risk countries | ❌ (Usually) | Allowed only with Government of India approval/treaty |
Currency Rules for GRCTCs in GIFT City: What’s Allowed and What’s Not
A Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC) operating in GIFT City IFSC is required to follow strict currency regulations as defined under the IFSCA Framework and aligned with India’s exchange control regime.
These rules are critical for compliance, accounting, and treasury system design.
Primary Rule: All Business Transactions Must Be in Freely Convertible Foreign Currency
GRCTCs must conduct all operational, investment, and financial transactions in freely convertible foreign currencies (e.g., USD, EUR, GBP, JPY). This rule ensures that IFSC units remain compliant with India’s non-resident financial zone structure.
Definition: A freely convertible currency is one that is fully exchangeable on the global forex market without regulatory restrictions typically those designated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Exception: INR Use for Administrative Expenses Only
GRCTCs may use Indian Rupees (INR) only for:
- Paying local administrative and operational expenses such as rent, salaries, utilities, and vendor payments within India
This is done through a Special Non-Resident Rupee (SNRR) account, which must be opened with an Authorized Dealer Category-I bank in India.
Important:
- SNRR accounts cannot be used for capital or investment transactions
- INR balances must not be used for onward lending or FX settlements
Non-Convertible Currency Transactions: Settled in Foreign Currency
If a transaction involves a currency that is not freely convertible (e.g., certain emerging market currencies), it must still be settled in a freely convertible foreign currency.
Derivatives in INR: Conditional Permission
Derivatives linked to INR (e.g., INR interest rate swaps, FX futures) are permitted only if:
- One leg of the transaction is denominated in a freely convertible foreign currency
- The purpose is related to treasury risk management or hedging for eligible group entities
Example: An INR-USD cross-currency swap is allowed. A standalone INR-INR derivative is not permitted.
Accounting, Reporting and Prudential Requirements for GRCTCs in GIFT City
1. Accounting and Reporting Obligations
Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centres (GRCTCs) in GIFT IFSC must follow specific financial reporting standards:
- Maintain books of accounts in a freely convertible currency (commonly USD)
- Maintain parallel INR accounts for compliance with Indian regulations
- Submit the following to the IFSCA within 90 days of the financial year-end:
- Audited financial statements
- Confirmation of compliance with applicable regulations
- Annual performance report
All financial reporting to IFSCA must be done in USD.
2. Prudential Norms Exemption
GRCTCs benefit from exemptions to standard prudential norms applicable to other finance companies in IFSC, including:
- Capital adequacy ratios
- Liquidity coverage ratios
- Exposure limits
These exemptions apply only if the GRCTC:
- Has a board-approved prudential policy
- Satisfies IFSCA’s fit and proper person criteria
This makes GRCTCs easier to operationalize and more efficient to maintain.
Advanced Cash Pooling Structures in GIFT IFSC
Cash pooling is a core function of any Global/Regional Corporate Treasury Centre (GRCTC), enabling efficient group-wide liquidity management. While IFSCA’s GRCTC framework allows intra-group pooling, detailed recognition of physical, notional, and cross-currency pooling is implied but not yet explicitly codified in the regulations.
What Types of Cash Pooling Can a GRCTC Undertake?
Treasury centres in GIFT City are permitted to implement the following pooling models, subject to group-only usage and compliance with foreign exchange regulations:
1. Physical Cash Pooling
- How it works: Surplus balances from group entities are physically transferred into a central treasury account.
- Regulatory status: Permitted, as long as funds flow between eligible group entities and align with FEMA/ODI norms.
- Use case: Daily sweeping of funds into the GRCTC from Indian or overseas subsidiaries.
2. Notional Cash Pooling
- How it works: Balances are virtually consolidated across group accounts, with no actual transfer of funds. Interest is calculated on a net basis.
- Regulatory status: While not yet explicitly defined by IFSCA, notional pooling is operationally feasible through virtual account structures and is used in global GRCTC setups.
- Use case: FX cost savings and liquidity optimization without changing legal ownership of funds.
3. Cross-Currency Cash Pooling
- How it works: Balances across different foreign currencies are aggregated and offset using internal exchange rates.
- Regulatory status: Subject to RBI and IFSCA FX rules, including reporting and currency convertibility.
- Use case: Managing multi-currency liquidity across USD, EUR, GBP, AED, and other convertible currencies.
Comparative Table: Cash Pooling Models in GIFT City
| Pooling Type | Fund Movement | Currency Scope | IFSCA Status | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Pooling | Actual transfers | Any permitted foreign currency | Explicitly permitted | Daily sweeping, real-time liquidity |
| Notional Pooling | No transfers | Multi-currency | Operationally feasible | FX savings, efficient interest netting |
| Cross-Currency Pooling | Actual/virtual | Convertible currencies | Permitted with compliance | Global treasury efficiency, FX control |
GRCTCs as Commodity Trading and Hedging Hubs
Beyond traditional cash and FX operations, GRCTCs in GIFT City can also centralize commodity trading and hedging functions for the group—unlocking strategic value across supply chains.
Permitted Use Case
- GRCTCs may act as commodity procurement and trading centers, managing pricing exposure across jurisdictions.
- Enables group-wide hedging of raw materials, energy, and metals through OTC or exchange-traded instruments (where allowed).
Industry Recommendation: Freight Rate Hedging
- Leading industry voices, including EY, advocate for explicit permission for freight rate hedging within GIFT’s treasury framework.
- Objective: Let Indian shipping and manufacturing groups hedge Bunker/Index-linked freight rates locally, instead of via Singapore or Dubai.
Compliance Snapshot
| Activity | Current Status |
|---|---|
| Commodity Hedging | Partially allowed (FX/IR permitted, commodities evolving) |
| Freight Rate Hedging | Industry-suggested; policy under review |
As the GRCTC framework evolves, these expansions could position GIFT City as a multi-dimensional treasury and trade risk management hub.
Industry Use Cases & Case Studies
The adoption of Global Treasury Centres (GTCs) in GIFT IFSC and Regional Treasury Centres (RTCs) in GIFT IFSC is gaining momentum across industries. Multinational corporations (MNCs) are recognizing the regulatory clarity, tax benefits, and cost advantages of setting up treasury hubs in India. Below are sector-specific use cases and case studies that demonstrate how different industries leverage corporate treasury services in GIFT City.
IT & ITES – Leveraging GIFT IFSC for Global Cash Flow Efficiency
India’s IT and IT-enabled services (ITES) sector contributes ~7.5% of GDP and generates over USD 250 billion in annual revenues (FY24), much of which comes from exports. This sector faces challenges in multi-currency inflows, FX volatility, and working capital deployment.
Use Case:
- Centralized treasury at GIFT IFSC manages multi-currency cash pooling from clients across the US, EU, and Asia.
- FX hedging through permitted derivatives mitigates risks from USD/INR volatility.
- Idle cash is deployed into foreign currency bonds and money market instruments, optimizing returns.
Example: Large IT service providers are exploring RTCs in GIFT City to consolidate export receivables and fund overseas subsidiaries, reducing reliance on multiple offshore hubs like Singapore and Dublin.
Pharma & Life Sciences – Managing Global Supply Chains
India is the world’s third-largest producer of pharmaceuticals by volume, exporting to 200+ countries. Pharma companies deal with complex supply chains, regulatory approvals, and high R&D investments, making treasury centralization critical.
Use Case:
- In-house banking from GIFT IFSC supports intercompany loans for subsidiaries managing R&D and global distribution.
- Treasury hubs issue External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) to finance expansion into regulated markets like the US and EU.
- Risk analytics platforms in GIFT City help forecast commodity and FX exposure for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Example: Mid-to-large Indian pharma players are actively evaluating GIFT IFSC as an alternative to their current Singapore treasury setups, driven by 10-year tax holidays and reduced dividend withholding tax at 10%
Manufacturing & Industrial – Financing Global Expansion
India’s manufacturing sector, supported by the Make in India initiative, is expected to reach USD 1 trillion by 2030. Global manufacturing firms operating in India face challenges in capital allocation, raw material price hedging, and cross-border liquidity.
Use Case:
- GTCs in GIFT City act as “funding hubs”, raising capital through bond issuances and syndicated loans.
- Commodity hedging via derivatives protects against volatility in steel, crude oil, and metals.
- Centralized payment factories streamline vendor and supplier payments across multiple jurisdictions.
Example: A large multinational automotive group is assessing GIFT City for its regional treasury centre for South Asia, aiming to reduce treasury costs by 30–40% compared to Singapore, while gaining direct access to India’s fast-growing debt and equity markets.
Industry-Wise Benefits of GTC/RTC in GIFT IFSC
| Industry | Treasury Need | GIFT City Advantage |
| IT/ITES | FX risk, idle cash deployment, export receivables | Multi-currency pooling, AI-driven risk analytics, tax-free surplus investments |
| Pharma | R&D funding, API supply chain risks, ECB financing | In-house banking, derivative access, 100% tax holiday on treasury income |
| Manufacturing | Capital allocation, commodity hedging, supplier payments | Bond/ECB fundraising, centralized payments, lower costs vs Singapore/Dubai |
Challenges & Considerations for GTC/RTC in GIFT City
While GIFT IFSC offers unmatched benefits for setting up a Global Treasury Centre (GTC) or Regional Treasury Centre (RTC), corporates must also evaluate the practical challenges before transitioning operations.
Need for Operational Readiness
- Companies require robust governance structures to centralize treasury activities without disrupting local operations.
- Standardization of intercompany loan agreements, treasury policies, and reporting formats is essential.
- A phased migration strategy helps avoid compliance risks and liquidity mismatches during setup.
Regulatory Compliance (FEMA, Companies Act, IFSCA)
- FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act): Treasury centres must align intra-group loans and FX transactions with FEMA guidelines.
- Companies Act, 2013: Reporting obligations such as board approvals, filings, and related-party disclosures remain relevant for Indian subsidiaries.
- IFSCA Regulations: While GIFT IFSC provides liberalized norms, entities must comply with prudential exposure limits, derivative guidelines, and disclosure requirements.
- Global corporates must also ensure compliance with OECD BEPS and global minimum tax frameworks, which affect treasury structuring.
Technology Infrastructure
A successful GTC/RTC depends on Treasury Management Systems (TMS) integrated with global ERPs.
Key requirements include:
- Real-time visibility of global cash balances
- Automated FX and derivatives execution
- Blockchain/APIs for faster reconciliation
MNCs must invest in cybersecurity protocols, as treasury hubs are high-value targets for cyberattacks.
Skilled Manpower Training
While India offers a large pool of finance professionals, specialized treasury skillsets (cash pooling, derivatives pricing, global compliance) are still developing.
Corporates setting up GTC/RTC in GIFT IFSC should:
- Invest in treasury certification programs (ACT, CFA, FRM)
- Upskill employees in AI/ML-driven risk analytics
- Build teams capable of 24/7 liquidity monitoring across time zones
Emerging Gaps: Trade Finance & Commodity Trading Regulation
- Trade Finance Expansion Needed: GIFT IFSC currently lacks full-scale trade finance tools like factoring, forfaiting, and receivables financing. Adding these would boost liquidity support for group entities.
- Commodity Trading Rules Absent: A formal framework for OTC and physical commodity trading is still missing, limiting participation by global hedging desks.
Future of GTC & RTC in GIFT IFSC
India as an Alternative to Singapore & Dubai
- With lower operating costs and tax-neutral structures, GIFT City is emerging as a cost-effective alternative to established hubs like Singapore and Dubai.
- By 2025, India aims to position GIFT IFSC as the preferred treasury centre for Asia, Middle East, and Africa, capitalizing on India’s trade linkages with these regions.
IFSCA Roadmap for 2030 – Treasury Flow Growth
- IFSCA projects treasury flows of USD 50+ billion by 2030 through GTCs and RTCs in GIFT IFSC.
- Key growth drivers:
- Expansion of multi-currency cash pooling.
- Increased bond issuances and ECBs.
- Adoption of green and ESG-linked financing.
Role in India’s Financial Globalization Strategy
- GIFT IFSC supports India’s vision of becoming a global financial powerhouse by 2047.
- By encouraging treasury centralization, GIFT City:
- Attracts foreign MNCs to manage Asia operations from India.
- Strengthens capital market depth through bond/FX activity.
- Enhances India’s role in cross-border trade and financial flows.
- With 580+ entities already registered and banking assets exceeding USD 52 billion (Dec 2023), treasury centres are expected to be a key pillar of India’s global financial integration.
GIFT IFSC is rapidly transforming into a preferred hub for Global and Regional Treasury Centres (GTCs & RTCs) by offering a powerful combination of regulatory clarity under IFSCA, competitive tax incentives, world-class infrastructure, and cost advantages over hubs like Singapore and Dubai. With treasury activities such as cash pooling, FX hedging, in-house banking, intercompany lending, and bond issuances now permitted, MNCs across IT/ITES, pharma, and manufacturing are leveraging GIFT City for operational efficiency and cross-border liquidity management. Backed by India’s projected USD 5 trillion economy by 2030 and IFSCA’s roadmap targeting USD 50+ billion in treasury flows by 2030, GIFT City is positioning itself as a cornerstone of India’s financial globalization strategy, enabling corporates to centralize treasury operations while unlocking new opportunities across Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
References:
- https://ifsca.gov.in/Document/8_SCB_GIFT_City_Treasury_Centre_CFO_Workshop_(2.2025).pptx
- https://api.giftgujarat.in/public/tool-guiedes-for-setting/DoingBusinessatIFSC.pdf
- https://www.pwc.in/ifsc/global-treasury-centres.html
- https://www.pwc.in/assets/pdfs/opportunities-in-gift-ifsc-2024-v1-final.pdf
- https://www.ey.com/en_in/insights/risk/how-india-is-enhancing-gift-city-s-value-as-a-global-corporate-treasury-hub
- https://www.grantthornton.in/globalassets/1.-member-firms/india/assets/pdfs/flyers/treasury_activities_in_ifsc_gift_city.pdf
FAQs on GIFT Treasury Centres
-
What is a GIFT Treasury Centre / GRCTC?
A GIFT Treasury Centre (also called Global / Regional Corporate Treasury Centre, or GRCTC) is a finance company or finance unit located in the GIFT IFSC that acts as an internal (in-house) treasury hub for its group entities. It handles treasury functions such as liquidity and cash management, intra-group funding, hedging, risk management, investments, and other financial operations.
-
Why locate a Treasury Centre in GIFT IFSC? What are the advantages?
GIFT City offers several benefits for treasury operations, including 100% income tax exemption for 10 out of 15 years, no GST on offshore transactions, low operating costs, unified regulation under IFSCA, access to India’s financial markets, and proximity to Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. It allows companies to centralize their treasury functions at a lower cost compared to hubs like Singapore or Dubai.
-
What is the difference between a Global Treasury Centre (GTC) and a Regional Treasury Centre (RTC)?
A Global Treasury Centre manages the entire group’s financial operations across all countries, while a Regional Treasury Centre focuses on a specific region such as Asia-Pacific or the Middle East. GTCs handle worldwide liquidity and capital allocation, whereas RTCs focus on localized liquidity management and compliance with regional regulations.
-
Who can establish a Treasury Centre in GIFT City?
Multinational corporations with Indian or foreign subsidiaries, large Indian companies with overseas operations, and financial institutions such as banks and NBFCs can set up treasury centres in GIFT City under the IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021.
-
What activities can a Treasury Centre perform in GIFT City?
Treasury Centres can engage in:
-
Cash pooling and liquidity management in multiple currencies
-
Intra-group loans and financing
-
Risk management through derivatives and hedging
-
Investment of surplus funds in bonds, government securities, and money markets
-
Fundraising through loans, bonds, and external commercial borrowings
-
In-house banking and centralized payment processing
-
-
What are the recent regulatory updates for Treasury Centres in GIFT City?
Recent reforms introduced flexibility for Treasury Centres, including the ability to transfer Indian contracts for a limited period (subject to approval) and a requirement to have at least five qualified professionals, including a Head of Treasury and Compliance Officer, stationed in GIFT IFSC. These changes encourage real operational presence while easing entry barriers.
-
Is the Indian Rupee allowed in Treasury Centre operations?
No. Treasury Centres in GIFT IFSC operate in foreign currencies only. INR transactions are generally not permitted except for limited administrative expenses.
-
How does a company register a Treasury Centre in GIFT City?
Companies must apply under the IFSCA (Finance Company) Regulations, 2021, meet eligibility criteria (group relationship, jurisdictional compliance), establish physical presence in GIFT IFSC, and obtain approval from IFSCA to commence operations.
-
What regulatory authority governs Treasury Centres in GIFT City?
The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) regulates all Treasury Centres in GIFT City. It provides a unified regulatory framework by consolidating powers of RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA.
-
Can a Treasury Centre lend or accept deposits from entities outside its group?
No. Treasury Centres are allowed to serve only their group entities. They cannot accept deposits or lend to unrelated third parties.
-
How does GIFT City compare to Singapore or Dubai for treasury operations?
GIFT City offers a lower-cost alternative to traditional hubs like Singapore and Dubai. It provides similar financial freedom and international access but with better tax incentives, regulatory clarity, and cost efficiency. It also gives corporates direct access to India’s growing capital markets.
-
What kind of staffing is required for a GIFT Treasury Centre?
Each Treasury Centre must employ at least five qualified professionals, including key positions such as Head of Treasury and Compliance Officer, based in GIFT IFSC.
-
What industries are best suited for Treasury Centres in GIFT City?
Industries such as IT & ITES, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, infrastructure, and financial services benefit the most. These sectors require multi-currency cash flow management, risk hedging, and access to global capital—all of which are efficiently supported by GIFT IFSC.
-
Can a Treasury Centre handle contracts or payments for Indian entities?
Primarily, Treasury Centres operate in foreign currency for offshore or group transactions. Limited exceptions may apply for Indian contracts subject to IFSCA approval.
-
How long does it take to set up a Treasury Centre in GIFT City?
Depending on readiness and approvals, it generally takes between 2 to 4 months to complete registration, infrastructure setup, and obtain IFSCA authorization.
-
How is a regional treasury centre different from a GTC?
A Regional Treasury Centre (RTC) focuses on specific geographies (such as Asia, Middle East, or Africa), while a GTC manages global operations.
- RTC: Provides localized liquidity support, FX hedging, and compliance with regional regulations.
- GTC: Oversees capital allocation, risk, and cash flows for the entire global footprint of the corporation.
In practice, many MNCs begin with an RTC and scale into a GTC as their treasury operations mature.
-
What tax benefits are available for corporate treasury services in GIFT City?
- 100% income tax exemption for 10 consecutive years out of 15.
- No GST on financial services rendered to offshore clients or other IFSC units.
- Interest income: Exempt when paid to non-residents.
- Dividend income: Taxed at only 10% for non-residents.
- Lower stamp duty and capital gains tax, reducing overall transaction costs.
-
Which companies are eligible to set up GTC/RTC in GIFT IFSC?
- Multinational corporations (MNCs) with overseas and Indian subsidiaries.
- Large Indian corporates with significant international operations.
- Financial institutions like banks, NBFCs, and fintechs offering treasury management solutions.
- Companies engaged in cross-border trade, IT/ITES exports, pharma supply chains, and manufacturing that require centralized treasury management.
-
How does GIFT City compare with Singapore and Dubai as a treasury hub?
- Tax Regime: GIFT IFSC offers a 100% tax holiday (10/15 years), vs Singapore’s 17% corporate tax (from 2025) and Dubai’s 0–9% corporate tax.
- FX Regulations: GIFT allows full convertibility in 15 foreign currencies (excluding INR), comparable to Singapore and Dubai.
- Cost of Operations: GIFT City provides 30–40% lower costs for office space, compliance, and skilled workforce compared to Singapore and Hong Kong
- Market Access: Unlike Singapore or Dubai, GIFT City offers direct access to India’s USD 3.94 trillion economy (FY24) and growing capital markets, making it a dual gateway for regional and global treasury operations.
-
Can my GRCTC in GIFT IFSC serve customers outside my group?
No. Only direct or indirect group entities are eligible. Public clients or unrelated entities are strictly prohibited.
-
What if one of my group entities is in a FATF grey-listed country?
FATF grey-list status doesn’t automatically disqualify, but enhanced due diligence may be required. Only blacklisted (“Call for Action”) jurisdictions are restricted.
-
Can I apply for a special exemption to serve a high-risk country entity?
Yes, but only if such an exemption exists under a formal Government of India agreement, treaty, or notification.
We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts


AIF in GIFT City IFSC- Structures, Regulations, Benefits
AI Summary The growth of Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) in…
Learn More





GIFT City Business Opportunities – A Deep Exploration
AI Summary GIFT City (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) is India’s…
Learn More





GIFT City Ecosystem for Startups – A Complete Guide in 2026
AI Summary GIFT City, India's first International Financial Services Centre…
Learn More














