AI Summary
The emergence of Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) in GIFT City IFSC represents a transformative shift in India's investment landscape, allowing fund managers to leverage a regulated and tax-efficient platform within India. Fund managers are relocating AIFs to GIFT City due to benefits such as foreign currency capital raising, unified regulation under IFSCA, expedited registration processes, and favorable tax treatment. GIFT City AIFs are now competitive with traditional offshore jurisdictions, combining international investment flexibility with onshore regulations. The structure supports diverse strategies, making it appealing for investors seeking unique asset classes. With a projection to reach USD 100 billion in commitments by 2030, GIFT City is poised to solidify its role as a leading hub for India-linked investments, especially in categories like hedge funds and private equity.
Last Updated on: 21st January 2026, 02:14 pm
Contents
- 1 Introduction: Why AIFs in GIFT City IFSC Matters Today
- 2 Introduction to Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) in GIFT City
- 3 About GIFT City IFSC
- 4 Regulatory Evolution of AIFs in GIFT City
- 5 Framework of AIF in GIFT City IFSC
- 6 Fund Management Entity (FME) – Concept, History and Role
- 7 Key Attributes of Fund Management Entities (FMEs) in GIFT City IFSC
- 8 Attributes of AIF Schemes in GIFT City
- 9 Types and Categories of AIFs in GIFT City
- 10 Minimum Requirements for AIF in GIFT City
- 10.1 Corpus and Investment Thresholds for AIFs
- 10.2 Sponsor or Manager
- 10.3 Minimum Requirements for Angel Funds in GIFT City IFSC
- 10.4 Angel Fund Corpus and Investor Investment Limits
- 10.5 Eligibility Criteria for Angel Investors
- 10.6 Investment Limits in Venture Capital Undertakings (VCUs)
- 10.7 Sponsor Commitment for Angel Funds
- 11 How AIFs in GIFT City Operate (Working Mechanism)
- 12 Permissible Activities and Investments of AIFs in GIFT City
- 13 Setting Up an AIF in GIFT City – Registration Process
- 14 Taxation of AIF in GIFT City IFSC
- 15 Attribution and Pass-Through Mechanism Explained
- 16 How NRIs and Foreign Investors Can Invest in GIFT City AIFs
- 17 GIFT City AIF vs Traditional Domestic AIF
- 18 Key Considerations for Fund Managers and Investors
- 19 Future Outlook of AIF in GIFT City IFSC
Introduction: Why AIFs in GIFT City IFSC Matters Today
The rise of AIF in GIFT City IFSC marks a structural shift in how India-linked alternative investment funds are being set up, managed, and scaled globally. What was earlier achieved through offshore jurisdictions is now increasingly being executed through GIFT City based AIFs, offering fund managers and investors a regulated, tax-efficient, and globally competitive platform within India’s IFSC framework.
Why Are Fund Managers Shifting AIFs to GIFT IFSC?
Fund managers are increasingly shifting AIF structures to GIFT City IFSC because it resolves structural inefficiencies present in both domestic and offshore fund models. Domestic AIFs face constraints around currency denomination, overseas exposure, and layered tax outcomes, while traditional offshore jurisdictions face rising compliance costs, substance requirements, and regulatory scrutiny. The GIFT City AIF framework offers a middle ground that is operationally efficient and regulatorily robust.
Key reasons driving this shift include:
- Ability to raise and deploy capital in foreign currency without conversion risk
- Unified regulation under IFSCA instead of multiple domestic regulators
- Faster fund and scheme registration timelines
- Tax pass-through benefits for Category I and II AIFs and clarity for Category III
- Simplified onboarding for non-resident and institutional investors
As a result, many India-focused and India-plus strategies that were earlier domiciled offshore are now being restructured as AIFs in GIFT City.
Is GIFT City Better Than Offshore Fund Jurisdictions?
For India-linked alternative strategies, GIFT City AIFs are increasingly competitive with, and in many cases superior to, traditional offshore fund jurisdictions. The key advantage lies in regulatory alignment and capital efficiency rather than location branding.
From a structural standpoint, GIFT City AIFs combine:
- Offshore-style investment flexibility
- Onshore regulatory certainty
- Access to India’s treaty network and IFSC-specific tax incentives
This has led to measurable adoption, particularly among hedge funds and trading-oriented strategies. Category III AIFs account for the fastest growth in GIFT City, reflecting the suitability of the IFSC framework for complex, leveraged, and cross-border investment strategies that previously relied on offshore hubs.
Key Data Snapshot: AIF in GIFT City IFSC (Updated 2026)
| Metric | Value |
| Operational IFSC | Since April 2015 |
| Regulator | International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) |
| Total registered entities | 1,034+ |
| Fund Management Entities (FMEs) | 194 |
| AIF schemes launched | 310 |
| Total commitments raised | USD 26.3+ billion |
| Capital deployed | USD 11+ billion |
| Fastest-growing category | Category III AIFs |
Introduction to Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) in GIFT City
Alternative Investment Funds have emerged as a critical capital vehicle for sophisticated investors seeking exposure beyond traditional stocks and bonds.
What Are Alternative Investment Funds?
An Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) is a privately pooled investment vehicle that raises capital from sophisticated investors and invests it according to a defined strategy that differs from traditional investment products such as mutual funds or bank deposits. AIFs are typically used for strategies that require flexibility, longer investment horizons, and access to non-traditional asset classes.
In India, AIFs are categorised into Category I, Category II, and Category III based on investment strategy and risk profile. When these funds are set up in GIFT City IFSC, they operate under a distinct IFSC framework that enables global capital participation and broader investment flexibility.
What Is an AIF in GIFT City?
An AIF in GIFT City IFSC is an Alternative Investment Fund registered with the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) and domiciled in India’s only operational International Financial Services Centre. Unlike domestic AIFs regulated by SEBI, these funds are structured to operate in foreign currency and are treated as non-resident for several regulatory purposes.
In practical terms, an AIF in GIFT City allows:
- Capital raising in USD or other freely convertible foreign currencies
- Investments into Indian assets through permitted routes and into overseas assets without domestic caps
- Participation by non-resident investors without typical offshore complexities
Asset Classes Typically Covered by AIFs in GIFT City
AIFs in GIFT City are widely used for diversified and complex strategies that require regulatory flexibility and global reach.
Common asset classes include:
- Private equity and venture capital, including growth-stage and buyout strategies
- Hedge funds and derivative strategies, particularly under Category III AIFs
- Real estate and infrastructure, including platform and yield-based investments
- Private credit and distressed assets, catering to structured and special situation opportunities
These asset classes benefit from the IFSC framework’s ability to support foreign currency funding, global counterparties, and institutional-grade governance.
How AIFs Differ From Mutual Funds
| Aspect | AIF in GIFT City | Mutual Fund |
| Investor type | Sophisticated and institutional | Retail-focused |
| Investment strategy | Flexible and complex | Highly regulated and limited |
| Currency | Foreign currency | Indian Rupees |
| Regulator | IFSCA | SEBI |
Regulatory Background: SEBI vs IFSCA
The regulatory distinction is central to understanding why AIFs in GIFT City function differently. Domestic AIFs are regulated by SEBI, with a framework primarily designed for India-centric capital flows. In contrast, AIFs in GIFT City are regulated by IFSCA, a unified regulator established under the IFSCA Act, 2019 to oversee all financial activities in the IFSC.
This shift in regulatory oversight enables:
- Globally aligned fund management regulations
- Centralised supervision instead of fragmented approvals
- Faster registration and scheme launch timelines
About GIFT City IFSC
GIFT City IFSC is India’s designated International Financial Services Centre, created to host financial services that are otherwise carried out offshore. From an AIF perspective, GIFT City acts as the jurisdictional platform that enables foreign currency fund operations within India.
Key characteristics relevant to AIFs include:
- Deemed foreign jurisdiction for FEMA, meaning transactions are treated as cross-border
- Operations entirely in freely convertible foreign currency
- Eligibility for SEZ-related benefits under the SEZ Act, 2005
Key Infrastructure Supporting AIFs in GIFT City
From an investment and fund operations standpoint, GIFT City hosts critical market infrastructure that supports AIF activity.
Relevant exchanges include:
- India INX, offering global securities and derivatives
- NSE IFSC, providing access to international equity and derivative products
- India International Bullion Exchange (IIBX), supporting bullion-linked strategies
Together, these features position the AIF in GIFT City as a globally competitive alternative investment structure that blends offshore efficiency with onshore regulatory certainty.
Regulatory Evolution of AIFs in GIFT City
The growth of AIFs in GIFT City IFSC has been driven by a deliberate and phased regulatory evolution aimed at positioning India as a competitive global fund management hub. From initial guidelines focused on enabling financial institutions to operate in a special economic zone, the framework has matured into a manager-led, globally aligned regime under a single regulator. This evolution has directly influenced fund manager adoption, investor confidence, and the rapid scale-up of AIF activity within the IFSC.
Timeline of Key Regulatory Milestones
The table below summarises the key regulatory developments that shaped the current AIF framework in GIFT City IFSC.
| Year | Regulatory Development | Impact on AIFs in GIFT City |
| 2015 | IFSC Guidelines and GIFT City operational | Established the legal foundation for financial institutions and funds to operate within an IFSC |
| 2018 | SEBI IFSC AIF Operating Guidelines | Provided the first dedicated framework for setting up and operating AIFs in GIFT City |
| 2019 | IFSCA Act enacted | Created a statutory authority to regulate all IFSC activities |
| 2020 | IFSCA becomes unified regulator | Replaced multi-regulator oversight with a single regulator for funds, banks, and capital markets |
| 2022 | IFSCA Fund Management Regulations | Shifted focus from fund-level regulation to manager-led regulation through FMEs |
| 2025 | Further simplification of fund management regime | Allowed retail participation and diversified fund products within IFSC |
Regulatory Evolution and Market Impact
This phased regulatory development directly correlates with the scale achieved by AIFs in GIFT City. As regulations matured, fund manager participation increased, leading to:
- 194 Fund Management Entities managing 310 AIF schemes
- USD 26.3+ billion in commitments raised
- Rapid growth in Category III AIFs, reflecting suitability for hedge fund and trading strategies
Framework of AIF in GIFT City IFSC
The framework of AIF in GIFT City IFSC is designed to support cross-border alternative investment strategies through a clearly defined institutional structure. Unlike domestic AIFs, where regulation is fund-centric, the IFSC framework is manager-led and globally aligned, ensuring operational efficiency, strong governance, and regulatory clarity. At a structural level, an AIF in GIFT City is established as a trust, company, or LLP and is managed by a registered Fund Management Entity (FME) under the supervision of the IFSC regulator. Capital is pooled from resident and non-resident investors, deployed across Indian and overseas assets, and administered through IFSC-based financial infrastructure.
How AIFs Are Structured in IFSC
The IFSC AIF structure is built to mirror mature offshore fund jurisdictions while retaining regulatory oversight within India. The framework separates ownership, management, custody, and administration functions, reducing conflicts of interest and enhancing transparency.
Core Components of an AIF in GIFT City IFSC
Sponsor
The sponsor is the promoter of the AIF structure and plays a critical role in establishing the fund’s credibility. The sponsor is required to maintain a minimum continuing interest in the fund, ensuring alignment with investor interests.
Key sponsor characteristics:
- Provides initial capital commitment
- Ensures compliance with eligibility and fit-and-proper criteria
Fund Management Entity (FME)
The Fund Management Entity (FME) is the central pillar of the AIF framework in GIFT City. Under the IFSC regime, FMEs are the primary regulated entities, responsible for investment management, risk oversight, and regulatory compliance.
Core responsibilities of an FME include:
- Portfolio construction and investment decision-making
- Compliance with IFSC fund management regulations
- Investor reporting and disclosures
- Appointment and oversight of service providers
As of 2025, 194 FMEs manage over 310 AIF schemes in GIFT City, reflecting the scalability of the manager-led framework.
Trustee or Board
Depending on the legal structure of the AIF, governance is provided either by a trustee or a board of directors. This layer ensures fiduciary oversight and protects investor interests.
Primary functions:
- Oversight of fund operations
- Monitoring compliance with fund documents
- Ensuring segregation of assets and proper governance
Custodian
The custodian is responsible for safekeeping of fund assets and settlement of transactions. For certain categories and corpus thresholds, appointment of an IFSC-compliant custodian is mandatory. For AIFs in GIFT City IFSC, appointment of a custodian is mandatory for all Category III AIFs, while for Category I and Category II AIFs it becomes mandatory only when the corpus of the scheme exceeds USD 70 million.
Custodian responsibilities include:
- Holding securities and financial assets
- Settlement and reconciliation of trades
- Independent verification of asset ownership
This role is particularly important for Category III AIFs and large institutional funds.
Administrator
The administrator handles operational and reporting functions, allowing the fund manager to focus on investment strategy. Administrators operating in GIFT City typically follow international fund administration standards.
Key administrative functions:
- Net asset value calculations
- Investor onboarding and record maintenance
- Capital call and distribution processing
- Periodic regulatory and investor reporting
Investors (Resident and Non-Resident)
The investor base for AIFs in GIFT City includes both resident and non-resident investors, subject to eligibility criteria. The framework is optimized for:
- Foreign institutional investors
- Non-resident Indians
- Indian residents investing under permitted outward investment norms
Minimum investment thresholds ensure that participation is limited to sophisticated investors, aligning risk profiles with complex alternative strategies.
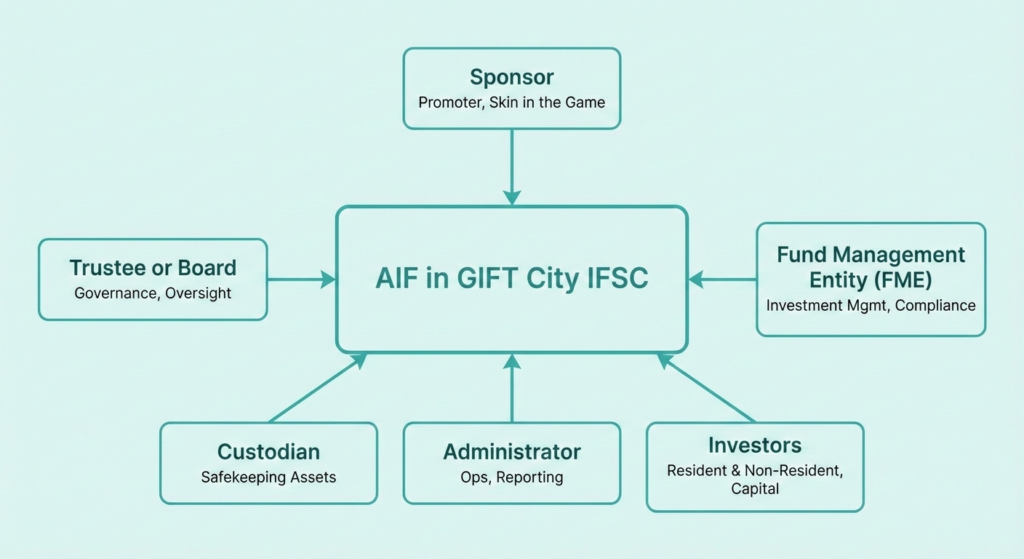

Image: Core components of GIFT City AIFs
Inbound and Outbound Investment Flow Model
The investment flow framework of an AIF in GIFT City supports both inbound and outbound capital movements in a single structure.
Simplified flow model:
- Capital is raised from global and domestic investors in foreign currency
- Funds are pooled at the AIF level in the IFSC
- Investments are made into:
- Indian assets through permitted investment routes
- Overseas assets without domestic allocation caps
- Returns are distributed and repatriated through IFSC banking channels
This dual-direction flow capability is a defining feature of the AIF framework in GIFT City IFSC, enabling fund managers to execute diversified and globally competitive investment strategies under a single regulated structure.
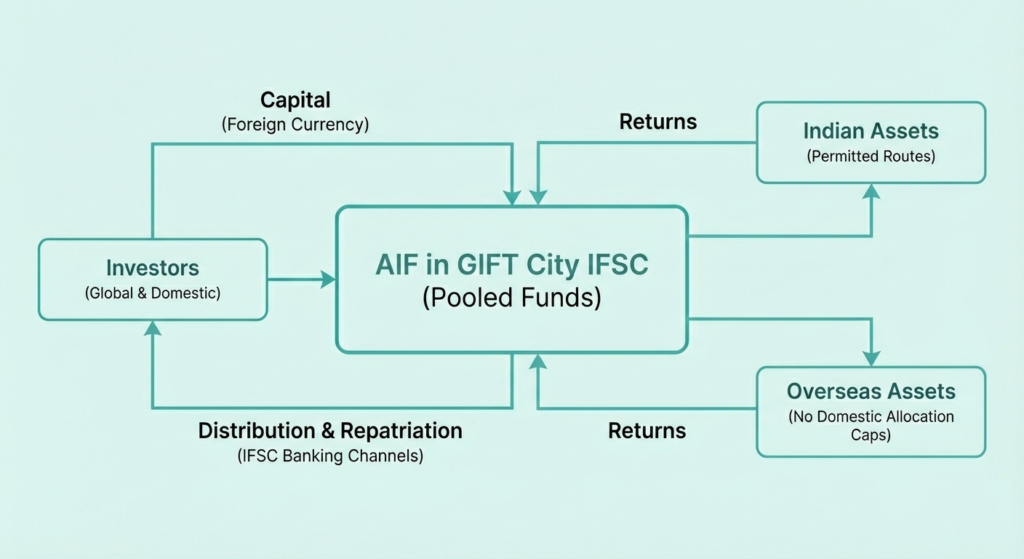

Fund Management Entity (FME) – Concept, History and Role
The Fund Management Entity (FME) is the cornerstone of the AIF in GIFT City IFSC framework. Unlike domestic AIF structures where regulation is primarily fund-centric, the IFSC model places the fund manager at the center of regulatory oversight. An FME is not the investment fund itself. Instead, it is the regulated entity responsible for managing one or more AIF schemes, overseeing investment decisions, risk management, compliance, and investor reporting.
What Is an FME?
A Fund Management Entity is a legal entity registered with the IFSC regulator to carry out fund management activities in GIFT City. The FME acts as the investment manager for AIFs and is accountable for all operational, fiduciary, and compliance obligations related to fund management.
Key characteristics of an FME include:
- It manages funds but does not hold investor assets directly
- It can manage multiple AIF schemes under a single registration
- It is the primary interface with the IFSC regulator
- It must meet prescribed net worth, governance, and staffing requirements
In the context of AIFs in GIFT City, the FME model significantly reduces duplication of compliance while improving oversight and institutional accountability.
History of FME Regulation in GIFT City
The introduction of FMEs marked a structural transformation in how alternative investment funds are regulated in the IFSC. Initially, AIFs in GIFT City followed a fund-centric regulatory approach similar to domestic frameworks. However, as the IFSC ecosystem matured, regulators recognized the need for a globally consistent model.
This led to a deliberate shift from fund-centric to manager-centric regulation, driven by policy recommendations and industry feedback. A key milestone in this transition was the Expert Committee Report submitted in January 2022, which laid the foundation for modern fund management regulations in the IFSC.
The outcome of this reform was:
- Clear separation between fund vehicles and management entities
- Greater accountability at the manager level
- Improved scalability for fund managers operating multiple strategies
Following these recommendations, the IFSCA Fund Management Regulations institutionalized the FME framework, making fund managers the principal regulated entities within GIFT City.
Categories of FMEs in GIFT City IFSC
To accommodate different investor profiles and fund strategies, the IFSC framework classifies FMEs into distinct categories based on the nature of investors served and the level of regulatory oversight required. Each category has defined eligibility and net worth requirements to ensure financial and operational resilience.
A Registered Retail FME or its holding company must demonstrate a minimum of five years of experience in fund or asset management and must have managed assets under management of at least USD 200 million with more than 25,000 investors, or alternatively, have at least one controlling person holding more than 25 percent shareholding with a minimum of five years of experience in financial services.
Types of Fund Management Entities
| FME Type | Eligible Investor Class | Minimum Net Worth |
| Authorised FME | Accredited investors and venture capital strategies | USD 75,000 |
| Registered FME (Non-Retail) | Accredited and institutional investors | USD 500,000 |
| Registered FME (Retail) | Retail and non-accredited investors | USD 1,000,000 |
Scheme Types Permitted by FME Category
| FME Category | Types of Schemes Permitted |
| Authorised FME | Venture Capital Schemes offered on a private placement basis |
| Registered FME (Non-Retail) | Venture Capital Schemes and Restricted Schemes offered on a private placement basis |
| Registered FME (Retail) | All schemes including Retail Schemes offered to all classes of investors |
Role of FMEs in the AIF Ecosystem
Across all categories, FMEs play a critical role in the success of AIFs in GIFT City IFSC by:
- Designing and executing investment strategies
- Ensuring regulatory compliance and risk controls
- Appointing and supervising custodians, administrators, and other service providers
- Maintaining investor disclosures and reporting standards
As of 2025, 194 FMEs actively manage more than 310 AIF schemes in GIFT City, underscoring the effectiveness of the manager-centric regulatory approach. This structure has enabled rapid ecosystem growth while maintaining governance standards comparable to leading global fund management hubs.
Key Attributes of Fund Management Entities (FMEs) in GIFT City IFSC
The Fund Management Entity (FME) is the regulated backbone of any AIF in GIFT City IFSC. To ensure strong governance, investor protection, and operational substance, the IFSC framework prescribes specific compliance attributes that every FME must meet. These requirements align GIFT City fund managers with global best practices while enabling scalable fund operations.
Core Compliance Requirements for FMEs
FMEs must be incorporated and operate within GIFT City IFSC, ensuring regulatory jurisdiction and operational substance.
Key attributes include:
- Legal structure: Company or LLP incorporated in GIFT City IFSC. Authorised FMEs and Registered Non-Retail FMEs may be set up as a company, LLP, or branch, whereas a Registered Retail FME is required to be incorporated only as a company under the IFSC framework.
- Operational presence: Adequate employees (including a principal officer and compliance officer) based in the IFSC
- Key Managerial Personnel (KMP): Minimum two, resident in India, with relevant fund management experience. Key Managerial Personnel of an FME must possess a professional qualification or a postgraduate degree or diploma of at least two years in fields such as finance, law, accountancy, business management, commerce, economics, capital markets, banking, insurance, or actuarial science from a recognised university, institution, or accredited professional body.
- Experience thresholds: Demonstrated expertise in managing alternative assets and investor capital
- Independent directors: Mandatory for FMEs managing retail AIF schemes
Minimum Staffing Requirements for FMEs in GIFT City IFSC
| FME Category | Minimum Employees Based in IFSC |
| Authorised FME | 1 employee designated as Principal Officer for overall activities |
| Registered FME (Non-Retail) | 2 employees consisting of one Principal Officer and one Compliance and Risk Manager |
| Registered FME (Retail) | 3 employees consisting of one Principal Officer, one Compliance and Risk Manager, and one additional Key Managerial Personnel for fund management |
Attributes of AIF Schemes in GIFT City
The attributes of AIF schemes in GIFT City IFSC are designed to balance investment flexibility with investor protection. Under the IFSCA framework, schemes are categorised based on investor type, risk profile, and investment strategy.
Scheme Categories under IFSCA
IFSCA classifies AIF schemes in GIFT City into three broad categories, each serving a distinct segment of the alternative investment market.
Venture Capital Schemes
Venture Capital Schemes are designed to support early-stage, growth-oriented, and innovation-driven investments. These schemes typically invest in start-ups, emerging companies, and high-growth sectors. Under the IFSC framework, venture capital schemes operate as restricted schemes and are targeted at sophisticated investors with higher risk tolerance and longer investment horizons.
Restricted Schemes (Open and Closed-ended)
Restricted Schemes form the core of AIF activity in GIFT City and are intended exclusively for sophisticated and institutional investors. These schemes may be structured as open-ended or closed-ended, depending on the liquidity profile and investment strategy.
Retail Schemes
Retail Schemes were introduced to expand the IFSC ecosystem beyond institutional capital. These schemes allow broader investor participation and include mutual funds, feeder funds, and ETF-linked structures. Due to their retail orientation, these schemes are subject to enhanced governance, disclosure, and risk management standards, offering lower risks.
Scheme-Level Regulatory Attributes by Scheme Type
IFSCA prescribes distinct structural, investor, and corpus-related conditions for Venture Capital Schemes, Restricted Schemes, and Retail Schemes established in GIFT City IFSC. These conditions determine the legal form, fund structure, investor participation limits, and minimum investment thresholds at the scheme level.
Comparative Overview of Scheme Attributes
| Parameter | Venture Capital Scheme | Restricted Scheme | Retail Scheme |
| Permissible legal structure | Company, LLP, or Trust | Company, LLP, or Trust | Company or Trust |
| Nature of scheme | Close-ended only | Open-ended or close-ended | Open-ended or close-ended |
| Minimum corpus | USD 5 million | USD 5 million | As prescribed for retail products |
| Maximum corpus | USD 200 million | No upper limit | Not applicable |
| Maximum number of investors | Fewer than 50 | Up to 1,000 or such higher limit as may be specified | No restriction |
| Maximum holding by a single investor | No limit | No limit | 25 percent of scheme corpus |
Minimum Investment by Investor Category
| Scheme Type | Investor Category | Minimum Commitment |
| Venture Capital Scheme | Accredited investors | No minimum threshold |
| Other investors | USD 250,000 | |
| Employees or partners of FME | USD 60,000 | |
| Restricted Scheme | Accredited investors | No minimum threshold |
| Other investors | USD 150,000 | |
| Employees or directors of FME | USD 40,000 | |
| Retail Scheme | Open-ended schemes | No minimum threshold |
| Close-ended schemes | USD 10,000 |
Key Attributes of AIF Schemes in GIFT City
| Attribute | Venture Capital Schemes | Restricted Schemes | Retail Schemes |
| Corpus limits | Minimum USD 5 million per scheme | Minimum USD 5 million per scheme | As prescribed for retail products |
| Number of investors | Limited to sophisticated investors | Limited and pre-identified investors | Broad retail investor base |
| Minimum ticket size | High minimum commitment | USD 150,000 per investor | Significantly lower thresholds |
| Asset classes | Start-ups and unlisted equity | PE, credit, real estate, hedge funds | Listed securities, ETFs, feeder funds |
| Leverage permissions | Generally not permitted | Permitted for Category III schemes | Restricted |
| NAV disclosure frequency | Periodic, as per scheme documents | Periodic and strategy-based | Frequent and standardised |
Sponsor / Manager Contribution Limits Linked to Targeted Corpus
| Targeted Corpus (TC) | Contribution Type | Venture Capital or Close-ended Non-Retail Scheme | Open-ended Non-Retail Scheme | Retail Scheme |
| Less than USD 30 million | Minimum | 2.5% of TC | 5% of TC | Lower of (a) 1% of AUM of the scheme or (b) USD 200,000 |
| Maximum | 10% of TC | 10% of TC | Not applicable | |
| More than USD 30 million | Minimum | USD 750,000 | USD 1,500,000 | Same as above |
| Maximum | 10% of TC | 10% of TC | Not applicable |
These contribution limits operate in addition to the general sponsor or manager continuing interest requirements and must be complied with at the scheme level. The upper cap of 10 percent of the Targeted Corpus applies to non-retail schemes to prevent excessive concentration of ownership.
Types and Categories of AIFs in GIFT City
The types and categories of AIFs in GIFT City IFSC are aligned with India’s alternative investment framework while incorporating IFSC-specific flexibility. These categories determine the investment strategy, risk profile, taxation treatment, and regulatory obligations of each fund. IFSCA recognises Category I, Category II, and Category III AIFs, along with a distinct framework for Angel Funds, each serving a specific segment of the alternative investment ecosystem.
Category I AIFs in GIFT City
Category I AIFs in GIFT City are focused on investments considered socially or economically desirable. These funds typically target long-term capital formation and innovation-led growth sectors.
Category I AIFs commonly invest in:
- Venture capital and start-ups
- Small and medium enterprises
- Infrastructure projects
- Social venture initiatives
From a structural perspective, these funds benefit from pass-through taxation, meaning income is taxed at the investor level rather than the fund level, except for business income where IFSC-specific tax holidays may apply.
Key regulatory attributes:
- Minimum corpus per scheme: USD 3 million
- Venture capital schemes: Minimum corpus of USD 5 million
- Long-term, closed-ended investment approach
Category I AIFs in GIFT City are widely used by global investors seeking early-stage exposure to India’s growth sectors within a regulated IFSC framework.
Category II AIFs in GIFT City
Category II AIFs form the largest segment of alternative funds in GIFT City IFSC. These funds cover strategies that do not fall under Category I or Category III and are typically used for institutional-grade investments.
Common strategies include:
- Private equity and buyout funds
- Private credit and debt funds
- Fund of Funds structures
Category II AIFs also enjoy pass-through taxation, providing tax efficiency for investors. However, these funds are subject to strict leverage restrictions, allowing borrowing only for day-to-day operational requirements.
Key characteristics:
- No investment incentives or concessions
- No leverage for investment purposes
- Designed for sophisticated and institutional investors
This category is particularly attractive for investors seeking predictable risk-return profiles and structured exposure to private markets.
Category III AIFs in GIFT City
Category III AIFs are designed for complex and high-frequency investment strategies and represent the fastest-growing category in GIFT City IFSC. These funds are commonly used for hedge fund and trading-oriented strategies that require flexibility and leverage.
Typical investments include:
- Hedge fund strategies
- Long-short equity and market-neutral strategies
- Derivatives and listed securities
Category III AIFs may be structured as open-ended or closed-ended funds, depending on liquidity needs. Unlike Category I and II, these funds are subject to fund-level taxation, with specific exemptions available for non-resident investors on eligible income streams.
Key features:
- Leverage permitted subject to regulatory limits
- Higher risk-return profile
- Strong appeal for global institutional investors
The IFSC framework has made Category III AIFs particularly competitive compared to offshore hedge fund jurisdictions.
Angel Funds in GIFT City IFSC
Angel Funds are a specialised sub-category designed to support early-stage businesses through pooled angel investments. GIFT City provides a clear regulatory framework for Angel Funds with defined eligibility and investment thresholds.
Key requirements include:
- Minimum corpus: USD 750,000
- Individual investor net tangible assets exceeding prescribed thresholds
- Corporate investor net worth meeting minimum limits
- Investment restrictions and caps in venture capital undertakings
Angel Funds in GIFT City allow structured participation in start-up investments while maintaining regulatory oversight and investor protection.
Table: Categories of AIFs in GIFT City
| Category | Key Strategies | Tax Treatment | Minimum Corpus |
| Category I | VC, SME, Infrastructure, Social Venture | Pass-through | USD 3M (VC: USD 5M) |
| Category II | PE, Debt, FoF | Pass-through | USD 3M |
| Category III | Hedge funds, derivatives | Fund-level taxation | USD 3M |
| Angel Funds | Start-ups and early-stage ventures | Category I treatment | USD 750,000 |
Minimum Requirements for AIF in GIFT City
The minimum requirements for AIF in GIFT City IFSC are prescribed to ensure financial robustness, investor sophistication, and alignment of interest between fund managers and investors. These thresholds apply at the scheme, investor, and sponsor levels and form the foundation of the IFSC AIF regulatory framework.
Corpus and Investment Thresholds for AIFs
Each AIF scheme in GIFT City must comply with the following minimum capital and investment requirements:
| Requirement | Amount |
| Minimum corpus per AIF scheme | USD 3,000,000 |
| Minimum investment by employees or directors of the AIF or its manager | USD 40,000 |
| Minimum investment by other investors | USD 150,000 |
The USD 3 million minimum corpus ensures economic viability of each scheme, while investor thresholds restrict participation to sophisticated capital. A lower threshold is permitted for employees or directors to promote internal alignment.
Sponsor or Manager
The IFSC framework mandates a minimum continuing interest to ensure that sponsors and managers maintain meaningful economic exposure to fund performance.
| AIF Category | Minimum Continuing Interest |
| Category I and Category II AIFs | Lower of 2.5 percent of corpus or USD 750,000 |
| Category III AIFs | Lower of 5 percent of corpus or USD 1,500,000 |
This contribution must be made in cash, maintained throughout the fund life, and cannot be fulfilled through management fee waivers.
Minimum Requirements for Angel Funds in GIFT City IFSC
Angel Funds operate under a specialised regime within the IFSC AIF framework, with distinct corpus, investor eligibility, and investment limits.
Angel Fund Corpus and Investor Investment Limits
| Requirement | Amount |
| Minimum corpus of Angel Fund | USD 750,000 |
| Minimum investment per angel investor | USD 40,000 |
| Maximum investment period | 5 years |
Eligibility Criteria for Angel Investors
| Investor Type | Eligibility Requirement |
| Individual | Net tangible assets exceeding USD 300,000, excluding principal residence |
| Body corporate | Net worth exceeding USD 1,500,000 |
Investment Limits in Venture Capital Undertakings (VCUs)
| Parameter | Limit |
| Maximum turnover of VCU | Below USD 3,750,000 |
| Industrial group turnover threshold | Below USD 45,000,000 |
| Minimum investment per VCU | USD 40,000 |
| Maximum investment per VCU | USD 1,500,000 |
Sponsor Commitment for Angel Funds
| Requirement | Amount |
| Sponsor or manager continuing interest | Lower of 2.5 percent of corpus or USD 80,000 |
This contribution must be maintained throughout the life of the fund and cannot be met through fee waivers.
How AIFs in GIFT City Operate (Working Mechanism)
The working mechanism of an AIF in GIFT City IFSC is designed to enable seamless cross-border capital movement, efficient deployment of funds, and predictable distribution of returns. At an operational level, a GIFT City AIF follows a clearly defined lifecycle. Capital is raised in freely convertible foreign currency, pooled under an IFSC-registered fund structure, deployed across Indian and overseas assets, and subsequently distributed to investors through IFSC banking channels.
How Does an AIF in GIFT City Work?
An AIF in GIFT City operates as a professionally managed pooled investment vehicle. The fund manager raises commitments from eligible investors, executes investments as per the stated strategy, and manages risk, reporting, and compliance under IFSC regulations.
Step-by-Step Investment Flow of a GIFT City AIF
1. Capital Raised in Foreign Currency
AIFs in GIFT City raise capital in USD or other freely convertible foreign currencies. This allows fund managers to align fund currency with underlying investments and reduces foreign exchange risk for global investors.
2. Investor Onboarding
Investors are onboarded following IFSC eligibility norms and compliance standards. The investor base typically includes:
- Foreign institutional investors
- Non-resident Indians
- Eligible resident investors under permitted outward investment limits
Robust KYC and onboarding processes ensure regulatory compliance and investor suitability.
3. Deployment of Capital
Once capital is pooled, the Fund Management Entity deploys funds in line with the scheme’s investment strategy.
Investment deployment may include:
- India-focused investments through permitted routes such as FDI, FPI, or FVCI
- Overseas investments without the caps applicable to domestic AIFs
This dual deployment capability is a defining feature of AIFs in GIFT City IFSC.
4. Income Distribution and Repatriation
Returns generated from investments are distributed to investors after accounting for expenses and applicable taxes. Repatriation is conducted through IFSC banking units, allowing smooth and timely transfer of funds to investors in their preferred currency.
Inbound vs Outbound Investment Structures for AIFs in GIFT City IFSC
AIFs established in GIFT City IFSC may be structured either as inbound investment vehicles, primarily pooling foreign capital for deployment into India, or as outbound investment vehicles, enabling resident Indian capital to access global markets through the IFSC. While both structures operate under the same regulatory framework, their investor base, FEMA treatment, and investment destinations differ.
Comparative Overview of Inbound and Outbound AIF Structures
| Parameter | Inbound Investment AIF | Outbound Investment AIF |
| Primary investor base | Foreign investors and non-residents | Resident Indian investors |
| Currency of investment | Freely convertible foreign currency | Freely convertible foreign currency |
| FEMA applicability | Minimal, as funds are non-resident | Subject to FEMA and LRS norms |
| Sponsor contribution | Permitted, subject to FEMA | Permitted, subject to FEMA |
| Role of IFSC AIF manager | Investment management and compliance | Investment management and compliance |
| Trustee involvement | Oversight and fiduciary supervision | Oversight and fiduciary supervision |
Permissible Investment Destinations
| Investment Category | Inbound AIF | Outbound AIF |
| Offshore securities, debt, derivatives, mutual funds | Permitted | Permitted |
| Securities listed on IFSC exchanges | Permitted | Permitted |
| Companies incorporated in IFSC | Permitted | Permitted |
| Indian listed and unlisted securities | Permitted via FDI, FPI, or FVCI routes | Not applicable |
| Units of AIFs, REITs, InvITs | Permitted | Permitted |
Investments between two AIFs set up in GIFT City IFSC are expressly permitted, subject to scheme objectives and applicable regulatory conditions.
Permissible Activities and Investments of AIFs in GIFT City
The permissible activities and investments of AIFs in GIFT City IFSC are intentionally broad, enabling fund managers to execute flexible, cross-border strategies under a regulated framework.
Permissible Investments for AIFs in GIFT City
AIFs in GIFT City IFSC may deploy capital across a wide range of asset classes and instruments, subject to scheme objectives and category-specific norms.
Permissible investments include:
- Securities listed on IFSC exchanges, supporting listed equity and derivative strategies
- Securities issued by Indian and foreign companies, listed or unlisted
- Units of other AIFs, enabling feeder and fund-of-funds structures
- REITs, InvITs, derivatives, and SPVs, supporting yield, infrastructure, and structured strategies
- Overseas entities and assets, without the investment caps applicable to domestic AIFs
This flexibility allows a single AIF in GIFT City to pursue India-only, overseas-only, or hybrid investment mandates.
Investment Restrictions by AIF Category
While the investment scope is broad, restrictions vary by AIF category to align risk levels with investor sophistication.
| AIF Category | Key Investment Restrictions |
| Category I | Focus on long-term and growth-oriented investments, no leverage |
| Category II | No leverage permitted except for operational requirements |
| Category III | Leverage and derivatives permitted within regulatory limits |
Setting Up an AIF in GIFT City – Registration Process
The AIF registration process in GIFT City IFSC follows a structured yet time-efficient pathway that integrates entity setup, SEZ approvals, and regulatory authorisation under a single IFSC ecosystem. The process is manager-centric, with regulatory focus on the Fund Management Entity, enabling faster scheme launches once core approvals are secured.
How to Register an AIF in GIFT City IFSC
Registering an AIF in GIFT City involves setting up the fund manager and fund vehicle, establishing physical presence in the IFSC, and obtaining approvals from the SEZ and IFSC authorities. The process is largely uniform across Category I, II, and III AIFs, subject to scheme-specific disclosures.
Step-by-Step AIF Registration Process in IFSC
1. Name Availability and Sponsor Identification
The process begins with finalising the sponsor and Fund Management Entity and confirming name availability for the AIF manager and sponsor entities.
2. Identification of Office Space in GIFT City
An office location within GIFT City IFSC is identified to meet substance and SEZ operational requirements.
3. Incorporation of Fund Manager and Fund Vehicle
The FME and AIF are incorporated as a company, LLP, or trust, based on the proposed structure and investor preferences.
4. Appointment of Trustee and Trust Deed Registration
Where the AIF is structured as a trust, a trustee is appointed and the trust deed is executed and registered.
5. SEZ and IFSC Approvals
Applications are submitted to the GIFT SEZ authorities and the Development Commissioner for approval to operate as an IFSC unit.
6. Registration with IFSC Regulator
The Fund Management Entity applies for registration with the IFSC regulator, providing details of governance, compliance framework, and key managerial personnel.
7. Scheme Launch and PPM Filing
Once the FME is authorised, individual AIF schemes are launched by filing the Private Placement Memorandum, outlining investment strategy, risks, and investor eligibility.
Typical Timeline for AIF Registration in GIFT City
| Stage | Indicative Timeline |
| Entity setup and SEZ documentation | Parallel process |
| Regulatory review and approvals | 2 to 3 months |
| Scheme launch after approval | Immediately post PPM filing |
NOTE: We have a detailed guide on Setting Up AIF in GIFT City
Taxation of AIF in GIFT City IFSC
The tax regime for AIFs in GIFT City IFSC is structured to deliver tax neutrality, investor certainty, and global competitiveness. Tax treatment varies based on AIF category, nature of income, and investor residency, with specific IFSC incentives reducing tax leakage at both fund and investor levels.
Tax Regime for Category I and Category II AIFs
Category I and Category II AIFs in GIFT City benefit from a pass-through taxation framework, under which income is generally taxed in the hands of investors rather than at the fund level.
Key tax features include:
- Pass-through status for all income other than business income
- Business income taxed at AIF level, eligible for a 100 percent tax holiday for 10 consecutive years out of the first 15 years under Section 80LA
- Non-resident investors exempt from tax on income arising from offshore investments made through the AIF
- Income retains its character at investor level, such as capital gains or interest
- Loss pass-through permitted for all losses other than business losses, subject to a minimum 12-month holding period of AIF units
- Business losses remain at the AIF level and may be carried forward by the fund
Additional investor-level benefits:
- Non-resident investors exempt from PAN and income tax return filing, subject to conditions and withholding compliance
- Ability to claim benefits under applicable tax treaties, where eligible
Tax Regime for Category III AIFs
Category III AIFs follow a fund-level taxation model due to their trading, leverage, and derivative-based strategies. However, the IFSC framework provides targeted exemptions for income attributable to non-resident investors.
Key tax attributes include:
- Fund-level taxation, with investor income generally exempt
- Exemption for income attributable to non-resident investors from:
- Transfer of offshore securities, debt instruments, derivatives, and specified IFSC-listed securities
- Securities issued by non-residents without a permanent establishment in India
- Eligible securitisation income
- Capital gains on Indian shares taxable at fund level:
- Short-term gains: 20 percent where securities transaction tax applies, otherwise 30 percent
- Long-term gains: 12.5 percent
- Interest and dividend income taxable at 10 percent, with lower rates available for specified debt instruments
- Surcharge capped at 15 percent on capital gains and dividend income
- MAT or AMT applicable at a concessional rate of 9 percent, significantly lower than standard domestic rates
- Income distributed by Category III AIF exempt in the hands of investors
Non-resident investors in Category III AIFs are also exempt from PAN and income tax return filing, subject to prescribed conditions.
Tax Benefits for AIFs and Managers in GIFT City IFSC
In addition to fund and investor-level benefits, the IFSC framework provides targeted incentives for fund managers and operations.
| Tax Benefit | Applicability |
| 100 percent tax holiday | Fund managers and FMEs for 10 out of 15 years |
| Reduced MAT or AMT | 9 percent for IFSC entities |
| GST exemption | Fund management and related services |
| STT and CTT exemption | Transactions on IFSC exchanges |
| Stamp duty exemption | Eligible IFSC transactions |
| Interest income exemption | Interest payable to non-residents on eligible borrowings |
Attribution and Pass-Through Mechanism Explained
The attribution and pass-through mechanism in AIFs in GIFT City IFSC determines how income earned by the fund is taxed in the hands of investors. This mechanism is central to the tax efficiency of IFSC-based AIFs, especially for Category I and Category II funds, where economic double taxation is avoided. Under the IFSC framework, income earned by the AIF is attributed directly to investors in proportion to their investment, except for specific categories of income.
How Is AIF Income Taxed to Investors?
For Category I and Category II AIFs in GIFT City, taxation generally occurs at the investor level rather than the fund level.
Key principles include:
- Income retains its original character when passed to investors
- Taxation depends on the residency status of the investor
- The AIF acts as a pass-through vehicle, not a taxable intermediary
This structure is particularly beneficial for non-resident investors participating in IFSC funds.
Business Income vs Capital Gains
The attribution mechanism distinguishes between types of income:
- Business income
- Taxed at the AIF level
- Eligible for IFSC-specific tax holiday benefits in applicable cases
- Capital gains, interest, and other income
- Passed through to investors
- Taxed in the hands of investors based on applicable rates and exemptions
This clear segregation provides predictability in tax outcomes for investors in AIFs in GIFT City.
Loss Pass-Through Rules
Losses other than business losses are also passed through to investors, subject to holding period conditions. Business losses, however, remain at the fund level and can be carried forward by the AIF as per applicable rules.
How NRIs and Foreign Investors Can Invest in GIFT City AIFs
NRIs and foreign investors are expressly permitted to invest in AIFs in GIFT City IFSC, making the IFSC a preferred jurisdiction for global capital targeting India-linked opportunities. The framework is designed to simplify participation while ensuring regulatory compliance.
FEMA and Investment Eligibility
From a regulatory standpoint:
- GIFT City is treated as a deemed foreign jurisdiction under FEMA
- Investments by NRIs and foreign investors are treated as non-resident investments
- No separate offshore structure is required
This classification removes many of the restrictions applicable to domestic investments.
LRS Applicability
- NRIs are not subject to Liberalised Remittance Scheme limits
- Resident Indians may invest subject to prescribed outward investment limits
This distinction makes GIFT City AIFs particularly attractive for non-resident capital.
Taxation for NRIs and Foreign Investors
Tax outcomes for NRIs investing in AIFs in GIFT City are highly favourable:
- Dividend income: Typically taxed at concessional rates ranging from 10 to 20 percent
- Capital gains: Exemptions available on eligible securities, particularly offshore assets
- Compliance relief: No requirement to obtain PAN or file income tax returns in India, subject to prescribed conditions
GIFT City AIF vs Traditional Domestic AIF
Choosing between a GIFT City AIF and a traditional domestic AIF depends on investment geography, investor base, currency preference, and tax efficiency. While both structures fall under India’s alternative investment framework, they are built for very different use cases. A GIFT City AIF is designed for cross-border capital and global strategies, whereas a domestic AIF primarily serves India-focused investments funded in INR.
Core Structural Differences Explained
A GIFT City AIF is regulated by a unified IFSC authority and functions in a deemed foreign jurisdiction. This enables fund managers to pool non-resident capital efficiently and invest both in India and overseas markets without the caps and approvals applicable to domestic AIFs. The tax regime is designed to be neutral and competitive, especially for non-resident investors.
A domestic AIF, regulated by SEBI, is suited for INR-denominated capital with a predominantly India-centric mandate. Overseas investments are permitted but subject to limits and approvals, and the tax regime follows standard domestic rules without IFSC-specific incentives.
High-Intent Comparison: GIFT City AIF vs Domestic AIF
| Parameter | GIFT City AIF | Domestic AIF |
| Regulator | IFSCA | SEBI |
| Operating currency | USD or foreign currency | INR |
| Tax regime | IFSC-specific incentives and exemptions | Standard domestic taxation |
| Overseas investment | Liberal and uncapped | Restricted and capped |
| FEMA applicability | Minimal due to deemed foreign status | Fully applicable |
Key Considerations for Fund Managers and Investors
The success of an AIF in GIFT City IFSC depends not only on regulatory advantages but also on how effectively fund managers and investors address operational, tax, and risk-related considerations.
Key Considerations for Fund Managers
For fund managers, operating an AIF in GIFT City requires building institutional-grade infrastructure aligned with IFSC regulations and global best practices. The manager-centric regulatory model places accountability squarely on the Fund Management Entity.
Critical considerations include:
- Compliance infrastructure to meet IFSC reporting, governance, and risk management standards
- Cross-border tax planning to ensure efficient structuring of India and overseas investments and distributions
- Custodian and governance standards, including appointment of independent custodians, administrators, and trustees where applicable
Managers must also ensure adequate on-ground substance in the IFSC, experienced key personnel, and scalable systems capable of supporting multiple schemes under a single FME.
Key Considerations for Investors
For investors, especially non-residents, AIFs in GIFT City offer attractive access to India and global markets. However, investment decisions should be guided by a clear understanding of jurisdictional and product-specific risks.
Key investor considerations include:
- Jurisdictional taxation, based on residency, income type, and applicable exemptions
- Liquidity and leverage risk, particularly in Category III and open-ended strategies
- Due diligence, covering fund manager track record, governance framework, service providers, and investment mandate
Future Outlook of AIF in GIFT City IFSC
The future outlook for AIFs in GIFT City IFSC remains strongly positive, supported by regulatory maturity, institutional participation, and expanding product scope. The ecosystem has already reached USD 26.3+ billion in commitments, and projections indicate accelerated growth over the coming decade.
Growth Projections and Market Trends
Key trends shaping the future include:
- Commitments projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 35 percent, targeting USD 100 billion by 2030
- Rising institutional adoption, including sovereign wealth funds, pension funds, and global asset managers
- Category III AIF dominance, driven by hedge fund and trading strategies suited to the IFSC framework
- Expansion into retail schemes and ETFs, broadening investor participation
- Increasing competitiveness with global fund hubs such as Singapore and Luxembourg
As regulations continue to evolve and infrastructure deepens, AIFs in GIFT City are positioned to become the default structure for India-linked and cross-border alternative investments. The combination of regulatory clarity, tax efficiency, and global credibility places GIFT City firmly on the map as a long-term international fund management destination.
FAQs on AIF in GIFT City IFSC
-
What makes an AIF in GIFT City IFSC different from offshore fund jurisdictions like Singapore or Mauritius?
An AIF in GIFT City IFSC combines offshore-style investment flexibility with onshore regulatory certainty. It allows foreign-currency fundraising, liberal overseas investments, and access to India’s tax treaty network under a single unified regulator, while avoiding rising substance and compliance burdens faced by traditional offshore hubs.
-
How does the Fund Management Entity (FME) model change AIF regulation in GIFT City?
GIFT City follows a manager-centric regulatory model, where the FME not the fund is the primary regulated entity. An FME can manage multiple AIF schemes under one license, reducing duplication, improving governance accountability, and enabling faster scaling compared to fund-centric SEBI AIF regulation.
-
What are the minimum corpus, investor commitment, and sponsor contribution requirements for a GIFT City AIF?
Each AIF scheme must have a minimum corpus of USD 3 million, with a minimum investor commitment of USD 150,000 (lower thresholds for employees/directors). Sponsors or managers must maintain a continuing interest ranging from 2.5% to 5% of corpus, depending on AIF category, paid entirely in cash.
-
How are Category I, II, and III AIFs taxed in GIFT City IFSC?
Category I and II AIFs enjoy pass-through taxation, with income taxed at the investor level (except business income, which may qualify for a 100% tax holiday under Section 80LA). Category III AIFs are taxed at the fund level but benefit from exemptions for non-resident investors, concessional MAT/AMT, and exemptions on eligible offshore income.
-
Can a GIFT City AIF invest both in India and overseas markets without allocation caps?
Yes. AIFs in GIFT City can invest in Indian assets through permitted routes (FDI, FPI, FVCI) and overseas assets without the caps applicable to domestic AIFs. This dual inbound-outbound investment capability is a defining structural advantage of the IFSC framework.
-
Are NRIs and foreign investors required to obtain PAN or file tax returns in India for GIFT City AIF investments?
In many cases, non-resident investors are exempt from PAN and Indian income tax return filing, subject to prescribed conditions and proper tax withholding. This significantly lowers compliance friction compared to domestic AIF investments.
-
Why are Category III AIFs and hedge fund strategies growing fastest in GIFT City?
Category III AIFs benefit from leverage permissions, derivatives trading, foreign-currency operations, and competitive IFSC tax exemptions, making GIFT City a strong alternative to offshore hedge fund jurisdictions for long-short, market-neutral, and trading-oriented strategies.
-
What is the typical timeline to set up and launch an AIF in GIFT City IFSC?
Once the Fund Management Entity and SEZ approvals are in progress, IFSCA registration typically takes 2–3 months, after which individual AIF schemes can be launched immediately upon filing the Private Placement Memorandum (PPM).
We Are Problem Solvers. And Take Accountability.
Related Posts


IFSCA Regulatory Newsletter – April 2025 to November 2025
Last Updated on: 15th December 2025, 07:04 pm
Learn More





Listing of Shares in GIFT City – Direct Listing at India INX & NSE IFSC
AI Summary GIFT City (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) is emerging…
Learn More





IPO Listing in GIFT City IFSC – Process, Eligibility, Benefits
AI Summary GIFT City is emerging as India's global IPO…
Learn More














