Author: Treelife
CBDT Notifies TDS Exemption for Payments to IFSC Units (Effective from July 1, 2025)
Payment Service Providers (PSPs) in GIFT City IFSCA
Overview of GIFT City and IFSC
What is GIFT City?
GIFT City (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) is India’s leading financial hub, designed to offer world-class infrastructure for financial institutions. Located in Gujarat, it aims to create a competitive environment for banking, insurance, capital markets, and fintech. GIFT City provides access to modern technology, regulatory flexibility, and a conducive business ecosystem for global financial services.
Role of IFSCA in GIFT City
The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) is the regulatory body overseeing financial services in GIFT City. IFSCA promotes and regulates financial services in the city, ensuring a global-standard environment with tax benefits and simplified compliance processes. By fostering an efficient regulatory framework, IFSCA attracts international businesses and investors to set up operations in GIFT City.
Significance of Payment Service Providers (PSPs) in the Evolving Fintech Landscape
Payment Service Providers (PSPs) play a pivotal role in the rapidly growing fintech ecosystem in India, particularly in GIFT City. PSPs are critical in facilitating secure and seamless digital transactions, both domestically and internationally. As India moves towards becoming a digital-first economy, PSPs are at the heart of this transformation, enabling businesses and consumers to conduct transactions more efficiently and securely.
Key Functions of PSPs in Fintech:
- Payment Processing: PSPs ensure smooth, real-time payments across various channels (e.g., mobile wallets, online payments, and cross-border remittances).
- Security and Compliance: PSPs maintain high standards of security protocols and adhere to regulatory norms to safeguard financial data and prevent fraud.
- Global Reach: With GIFT City’s global outlook, PSPs in the region can offer cross-border payment solutions, connecting international markets with India’s growing digital economy.
- Financial Inclusion: By enabling easy access to digital payments, PSPs contribute to financial inclusion, allowing a broader segment of the population to engage in the digital economy.
As the fintech space evolves, GIFT City has emerged as a prime location for both international and domestic PSPs to operate and grow, thanks to its robust regulatory environment, tax incentives, and access to a wide range of financial services.
Understanding Payment Service Providers (PSPs)
What are Payment Service Providers (PSPs)?
Payment Service Providers (PSPs) are intermediaries that enable businesses and consumers to conduct digital financial transactions securely and efficiently. PSPs handle the complexities of payment processing, ensuring seamless transactions between buyers, sellers, and financial institutions. They play a vital role in facilitating e-commerce, mobile payments, and international transactions, serving as the backbone of today’s digital payment ecosystem.
In simple terms, PSPs provide the technology and infrastructure necessary for processing payments, whether through credit cards, digital wallets, bank transfers, or other methods. As digital payments become more common, the role of PSPs becomes even more critical in ensuring secure, timely, and efficient transactions.
Role of PSPs in the Global and Indian Financial Ecosystem
PSPs are integral to both the global and Indian financial systems, enabling businesses to accept payments from customers worldwide. The role of PSPs includes:
- Facilitating cross-border payments: PSPs bridge the gap between different countries and currencies, allowing businesses to engage in international trade and customers to make payments seamlessly.
- Driving digital payments growth: With the shift to digital platforms, PSPs are central to enabling online transactions, particularly in the context of cross border remittances, escrow services, etc.
PSPs are essential for extending India’s digital payment revolution at a global stage, considering the success of platforms like Google Pay, PhonePe, and Paytm which has led to a surge in online transactions domestically..
Different Types of PSPs in GIFT City
PSPs come in various forms, each offering a specific set of services to meet the needs of businesses and consumers. Here are the primary types:
- Cross border Remittance Service Providers
- Cross border Remittance service providers enable cross-border money transfers, helping individuals send money to their families or businesses to transfer payments internationally.
- Cross border Remittance service providers enable cross-border money transfers, helping individuals send money to their families or businesses to transfer payments internationally.
- E-money issuance Services
- E–money issuance services allow users to store, send, and receive funds digitally. These platforms can be used for online shopping, bill payments, and peer-to-peer transfers.
- E–money issuance services allow users to store, send, and receive funds digitally. These platforms can be used for online shopping, bill payments, and peer-to-peer transfers.
- Merchant Acquisition services
- Merchant acquisition services the processing of card payments for businesses. They enable businesses to accept payments via credit or debit cards through Point-of-Sale (POS) systems or online payment systems.
- Merchant acquisition services the processing of card payments for businesses. They enable businesses to accept payments via credit or debit cards through Point-of-Sale (POS) systems or online payment systems.
- Escrow Services
- These are services where a third party holds funds in a secure account until the transaction conditions are met.
- These are services where a third party holds funds in a secure account until the transaction conditions are met.
Significant Payment Service Providers (SPSPs)
Significant Payment Service Providers (SPSPs) are entities that have a major impact on the market, either due to their size, scale, or operational reach. These PSPs are subject to stricter compliance and oversight standards to ensure that their operations remain transparent and secure.
Conditions for PSPs to be Designated as Significant PSPs:
| Criteria | Condition | Threshold |
| Payment Services | The PSP must provide one or more payment services (excluding e-money account issuance service) | $2 million (for one service) or $4 million (for two or more services) |
| E-money Account Issuance Service | If the provider offers e-money account issuance | Average daily value of all e-money stored exceeds $3 million |
| E-money Issuance Service | If the provider offers e-money issuance service | Average daily value of e-money issued exceeds $3 million |
Note:
- All thresholds are calculated based on averages over a calendar year.
- The values are measured in Specified Foreign Currency.
Regular Payment Service Providers (RPSPs)
Regular Payment Service Providers (RPSPs) are entities that offer designated payment services but do not meet the criteria to be classified as significant PSPs. These providers contribute to the financial ecosystem by offering various payment services but do not have the same level of operational impact as significant PSPs.
Eligible Activities of RPSPs:
- Account Issuance Service (including e-money account issuance)
- E-money Issuance Service
- Escrow Service
- Cross-Border Money Transfer Service
- Merchant Acquisition Service
RPSPs can still play a pivotal role in the economy by enabling small to medium-sized businesses to accept payments digitally and offer financial services in niche markets.
Net worth
| Type of Provider | Initial Net Worth Requirement | Net Worth Requirement by 3rd Financial Year |
| Regular Payment Service Provider | Regular Payment Service ProviderUSD 100,000 (or equivalent in a specified foreign currency) | USD 200,000 (or equivalent in a specified foreign currency) |
| Significant Payment Service Provider | USD 250,000 (or equivalent in a specified foreign currency) | USD 500,000 (or equivalent in a specified foreign currency) |
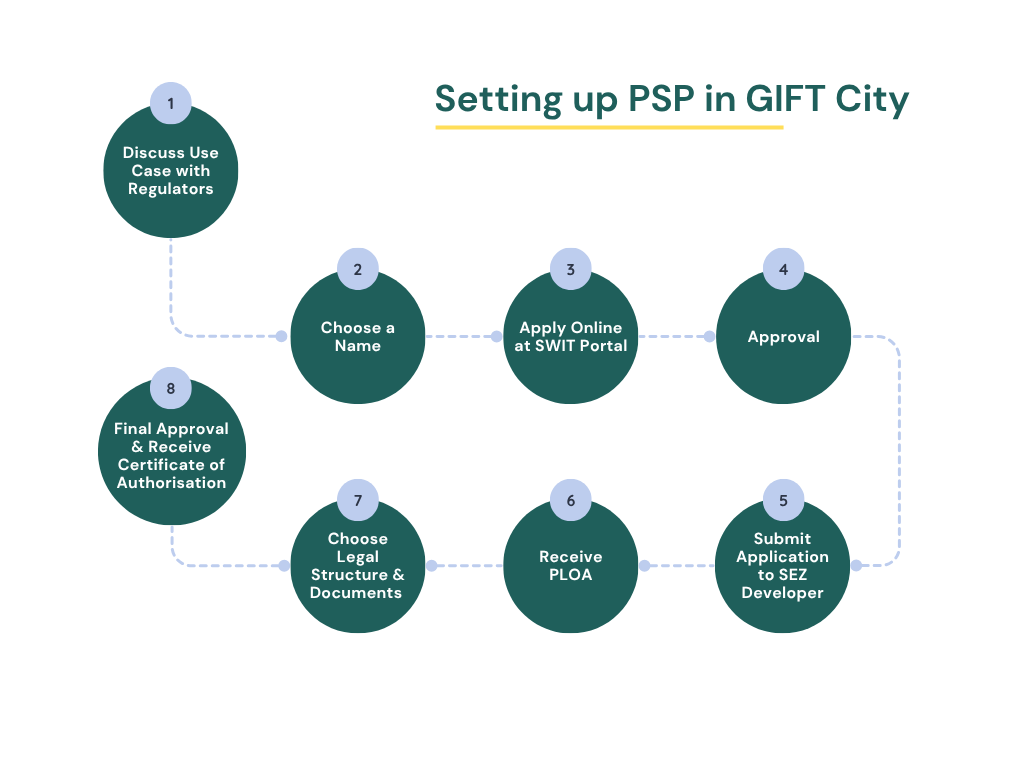
Setting Up Payment Service Providers (PSPs) in GIFT City 2025 – Steps
Setting up a Payment Service Provider (PSP) in GIFT City involves a structured process with several steps. Each step is crucial for ensuring legal compliance and operational readiness. This guide outlines the steps involved in setting up a PSP in GIFT City, starting from engaging with regulators to commencing operations.
STEP 1: Pre-Registration Process
- Discuss Use Case with Regulators
- Initial Consultation: Before applying, businesses must first discuss their use case with the regulators, ensuring that the business model complies with GIFT City’s regulatory framework. Engaging with regulators early ensures that the proposed operations align with the requirements set by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA).
- Initial Consultation: Before applying, businesses must first discuss their use case with the regulators, ensuring that the business model complies with GIFT City’s regulatory framework. Engaging with regulators early ensures that the proposed operations align with the requirements set by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA).
- Name Reservation for New Company
- Legal Requirements for Name Registration: The name must be unique and should not conflict with existing entities. It should also align with GIFT City’s branding guidelines.
- Steps to Reserve a Company Name in GIFT City:
- Choose a Name: Select a name that reflects your business type and aligns with the brand of GIFT City.
- Apply Online: Submit your application via the SWIT portal (GIFT City’s official registration platform).
- Approval: Once approved, the name will be reserved for a specified period during which company incorporation must be completed.
- Legal Requirements for Name Registration: The name must be unique and should not conflict with existing entities. It should also align with GIFT City’s branding guidelines.
- Premises Allotment and Issuance of PLOA (Possession Letter of Allotment)
- Role of SEZ Developer: The SEZ developer plays a crucial role in providing the land and premises within GIFT City. They will assist in the allocation of office space and ensure the property adheres to SEZ regulations.
- How to Obtain PLOA in GIFT City:
- Submit Application: Apply for office space allocation through the SEZ developer.
- Document Submission: Provide necessary documents such as your company’s incorporation certificate and proof of address.
- Receive PLOA: Once approved, you will receive the Possession Letter of Allotment (PLOA), confirming your right to occupy the premises.
- Role of SEZ Developer: The SEZ developer plays a crucial role in providing the land and premises within GIFT City. They will assist in the allocation of office space and ensure the property adheres to SEZ regulations.
- Incorporation of the Company
- Legal Structure for Setting Up a PSP: Most PSPs opt for a Private Limited Company or Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) as the legal structure.
- Essential Documents Required:
- Memorandum of Association (MoA) and Articles of Association (AoA)
- Identity and address proofs of directors
- Business plan outlining the services offered
- PLOA from the SEZ developer
- Legal Structure for Setting Up a PSP: Most PSPs opt for a Private Limited Company or Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) as the legal structure.
STEP 2: Application and Approval Process
- Application Before SEZ (IFSCA Admin) and IFSCA via SWIT Portal
- Detailed Explanation of the Application Procedure:
- Submit Application: Submit the detailed application via the SWIT portal, describing your business and the proposed PSP operations.
- Application Form: Provide information about your company, key personnel, business structure, and services.
- Key Documents Required:
- Company incorporation certificate
- PLOA
- Business plan and financial details
- KYC details for directors and shareholders
- Detailed Explanation of the Application Procedure:
- Review and Grant of In-Principle Approval
- What is In-Principle Approval, and Why is it Crucial?: In-principle approval is a preliminary step by IFSCA that confirms the initial acceptance of the business model and operations plan, moving the application closer to final approval.
- Timeline and Expected Steps Post-Approval:
- Approval Timeline: The in-principle approval process typically takes 4 to 6 weeks.
- Post-Approval Steps: After obtaining in-principle approval, businesses must meet certain regulatory requirements to advance to the final approval stage.
- What is In-Principle Approval, and Why is it Crucial?: In-principle approval is a preliminary step by IFSCA that confirms the initial acceptance of the business model and operations plan, moving the application closer to final approval.
STEP 3: Final Approval and Certification
- Complying with IFSCA Conditions for Final Approval
- Key Conditions to Be Met for Final Certification:
- Ensure compliance with all IFSCA regulatory requirements.
- Submit final documentation, including tax filings, operational plans, and internal controls.
- Role of IFSCA in Ensuring Compliance: IFSCA conducts thorough checks to ensure that your company complies with financial, operational, and data security regulations.
- Key Conditions to Be Met for Final Certification:
- Granting of Certificate of Authorisation (Final Approval)
- What Does the Certificate of Authorisation Signify?: The Certificate of Authorisation signifies that the PSP is fully authorized to operate within GIFT City under IFSCA’s regulations.
- Post-Approval Steps and Timelines: Upon receiving the Certificate of Authorisation, PSPs can begin their operations. However, they must meet final operational readiness checks within six months.
- What Does the Certificate of Authorisation Signify?: The Certificate of Authorisation signifies that the PSP is fully authorized to operate within GIFT City under IFSCA’s regulations.
STEP 4: PSP Operation Commencement in GIFT City
- Commencing Operations Within Six Months
- Overview of Operational Readiness: After final approval, PSPs must ensure that all operational infrastructure, such as payment systems and customer support, is set up and functioning.
- Final Checklist for Beginning PSP Services in GIFT City:
- Install technology infrastructure (payment gateways, security systems, etc.)
- Set up a local team for operations and customer service
- Test payment systems and security protocols
- Complete all legal and tax registrations to comply with GIFT City regulations
- Overview of Operational Readiness: After final approval, PSPs must ensure that all operational infrastructure, such as payment systems and customer support, is set up and functioning.

Payment Service Providers(PSPs) Regulation in GIFT City
Regulatory Framework for Payment Service Providers in GIFT City
GIFT City offers a comprehensive regulatory framework designed to support Payment Service Providers (PSPs), governed by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA). This framework aims to foster innovation while ensuring PSPs comply with global standards for financial services.
IFSCA Regulatory Guidelines for PSPs
- Overview of IFSC Regulations for PSPs:
- IFSCA provides a flexible yet robust regulatory structure for PSPs, offering a favorable environment for businesses engaged in payments, remittance services, e-wallets, and digital financial services.
- The regulations are tailored to ensure that PSPs operate efficiently, with a focus on financial integrity, consumer protection, and market stability.
Key Compliance Requirements for PSPs in GIFT City
PSPs must meet specific compliance obligations to operate in GIFT City:
- Know Your Customer (KYC): PSPs must implement strict KYC protocols to verify the identities of customers and prevent fraud.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML): PSPs are required to have measures in place to detect and prevent money laundering activities.
- Data Security: Compliance with data protection laws is essential, ensuring customer data is secure and transactions are protected.
- Operational Requirements: PSPs must establish robust financial systems to handle transactions, settlements, and reconciliations efficiently.
Payment Service Providers’ Operational Requirements
- Mandatory Licenses and Registrations:
- PSPs must obtain licenses from IFSCA to provide payment services, including remittance and digital wallet operations.
- PSPs must obtain licenses from IFSCA to provide payment services, including remittance and digital wallet operations.
- Ongoing Compliance and Reporting Obligations:
- PSPs in GIFT City must adhere to ongoing reporting and audit requirements, including regular financial disclosures, compliance reports, and updates on operations.
- Regular inspections by IFSCA ensure that PSPs remain compliant with all regulatory standards.
Tax Benefits for PSPs in GIFT City
One of the most attractive aspects of setting up a PSP in GIFT City is the tax incentives and financial benefits that businesses can leverage. These incentives are designed to encourage growth, innovation, and investment within the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC).
Tax Incentives in GIFT IFSC
- Income Tax Exemptions and Deductions Available for PSPs:
- 100% Income Tax Exemption for any ten consecutive years out of first fifteen years of operation
- GST Exemption on services provided within GIFT IFSC and abroad.
- Other Financial and Operational Incentives:
- No Minimum Tax: PSPs operating in GIFT City are not subject to minimum taxes, enhancing profitability where the PSPs are opting for a beneficial taxation regime.
- Customs Duty Exemptions: Businesses can import equipment and technology needed for payment processing without incurring customs duties subject to conditions.
FEMA Compliance and Guidelines for PSPs in GIFT IFSC
- Cross-Border Financial Regulations for PSPs:
- FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act) ensures that cross-border transactions adhere to India’s foreign exchange guidelines, enabling PSPs to process international payments smoothly.
- PSPs must comply with IFSC regulations and FEMA guidelines when dealing with foreign currency transactions and international money transfers pertaining to resident indians.
- Foreign Exchange Management for International Transactions:
- PSPs are required to manage foreign exchange operations in compliance with FEMA regulations, ensuring that foreign currency transactions are handled efficiently and securely.
- PSPs in GIFT IFSC can offer foreign exchange services for global transactions, remittances, and cross-border payments with fewer regulatory barriers compared to other regions in India.
Minimum Net Worth Requirements
The net worth requirements for Payment Service Providers (PSPs) in GIFT IFSC depend on whether they are classified as a Regular or Significant PSP.
| Category | Minimum Net Worth Requirement | Timeline |
Regular PSP | ₹8,200,000 (on commencement) | At start of operations |
| ₹16,400,000 (by end of the third financial year) | By March 31 (third year) | |
Significant PSP | ₹20,500,000 (within 90 days of designation) | Within 90 days of designation |
| ₹41,000,000 (by end of the third financial year) | By March 31 (third year) |
Regulatory Fees for PSPs in GIFT IFSC
IFSCA Fees
| Particulars | Regular PSP | Significant PSP | Payment System Operators (PSO) |
| Application Fees (One-Time) | USD 1000 | USD 1000 | USD 1000 |
| Authorization Fees | USD 25,000 (One-Time) | USD 25,000 (One-Time) | (a) Real time or deferred large value payment system – USD 15,000(b) Trade Repository – USD 5,000(c) Issuers of Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) – USD 10,000(d) Card Payment Networks – USD 15,000(e) TREDS platforms authorised under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 – USD 5,000(f) Any Other – USD 15,000 |
| Recurring Fees | USD 5,000 (Annual) | USD 10,000 (Annual) | (a). Real time or deferred large value payment system – USD 10,000(b). Trade Repository – USD 5,000(c). Issuers of Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) – USD 5,000(d). Card Payment Networks – USD 15,000(e). TREDS platforms authorised under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 – USD 10,000(f). Any Other – USD 10,000 Note: All the fees mentioned above is on annual basis |
SEZ Authorities’ Fees
| Particulars | Amount (INR) |
| Application Fees (One-Time) | ₹5,000 |
| Registration Fees (One-Time) | ₹25,000 |
| Recurring Fees (Annual) | ₹5,000 |
These net worth requirements and regulatory fees ensure that PSPs in GIFT IFSC are financially stable and compliant with local regulations.
Main Functions of Payment Service Providers (PSPs)
Payment Service Providers (PSPs) play a critical role in enabling businesses to accept payments and manage financial transactions. Their main functions include:
- Payment Processing: Facilitates businesses and merchants in receiving payments via credit and debit cards from customers.
- Global Transactions: Ensures safe, efficient, and cost-effective international transactions, solidifying GIFT City as a key fintech hub.
- Digital Wallets & Prepaid Cards: Provides consumers with digital wallets and prepaid cards to carry, send, and spend virtual money seamlessly.
Pre-Requisites for PSPs in GIFT IFSC
Before applying for approval in GIFT City, PSPs must meet the following requirements:
- Infrastructure: Adequate office space, equipment, and communication facilities within the GIFT City investment zone.
- Net Worth: Must satisfy the financial net worth criteria.
- Financial Soundness: Applicants must demonstrate financial stability and meet fit and proper requirements.
- Authorization History: The applicant or its affiliates must not have been denied authorization in the past.
- Relevant Experience: The applicant’s team must have adequate experience, including previous authorizations for similar services.
Why Set Up Payment Service Providers (PSPs) in GIFT City IFSCA?
GIFT City is a prime location for Payment Service Providers (PSPs) looking to establish themselves in India. With its unique offerings, GIFT City supports fintech businesses with regulatory benefits, tax incentives, and world-class infrastructure.
Regulatory Benefits: IFSCA’s Role in Providing a Regulated Environment
IFSCA provides a transparent and business-friendly regulatory framework, simplifying licensing and ensuring global compliance for PSPs. This regulatory support fosters a stable and secure environment for PSPs to scale their operations.
- Simplified Licensing: Fast-tracked approval process.
- Global Compliance: Adherence to international standards.
- Flexible Operations: Room for innovation while maintaining compliance.
Tax and Legal Benefits: Incentives in GIFT City
GIFT City offers a range of tax advantages and legal incentives that make it attractive for PSPs:
- Tax Exemptions: Income tax exemptions for the first five years.
- Reduced GST: Lower tax rates reduce operational costs.
- No Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT): Exemption on dividend distribution.
These benefits help PSPs improve profitability and operational efficiency.
International Reach: GIFT City’s Strategic Location
Located at the crossroads of India and global markets, GIFT City offers PSPs access to international clientele and business opportunities.
- Cross-Border Payments: Enables global payment solutions.
- Global Exposure: Attracts international investors and partners.
This strategic positioning helps PSPs expand their reach and grow internationally.
Technology and Infrastructure: Cutting-Edge Support for Fintech
GIFT City boasts advanced infrastructure that supports fintech businesses, including PSPs.
- Smart City Features: High-speed internet and data centers.
- Dedicated Fintech Ecosystem: Modern office spaces and tech parks.
- Advanced Payment Systems: Secure and efficient payment processing.
With world-class infrastructure, PSPs can scale their operations smoothly and securely.
How Treelife is a leading PSP Player in GIFT City
Treelife offers expert guidance for setting up a Payment Service Provider (PSP) in GIFT City, ensuring smooth entry into the IFSC ecosystem. We assist with obtaining necessary licenses from IFSCA and RBI, company registration, and structuring, while optimizing tax benefits under the GIFT City regime. Our services also cover compliance with KYC, AML regulations, and ongoing legal and financial support.
IFSCA Notifies Updated Regulations for Capital Market Intermediaries in IFSC
IFSCA Eases Staffing Requirements for GRCTCs in IFSCs
Family Office in GIFT IFSC & Setting up FIF
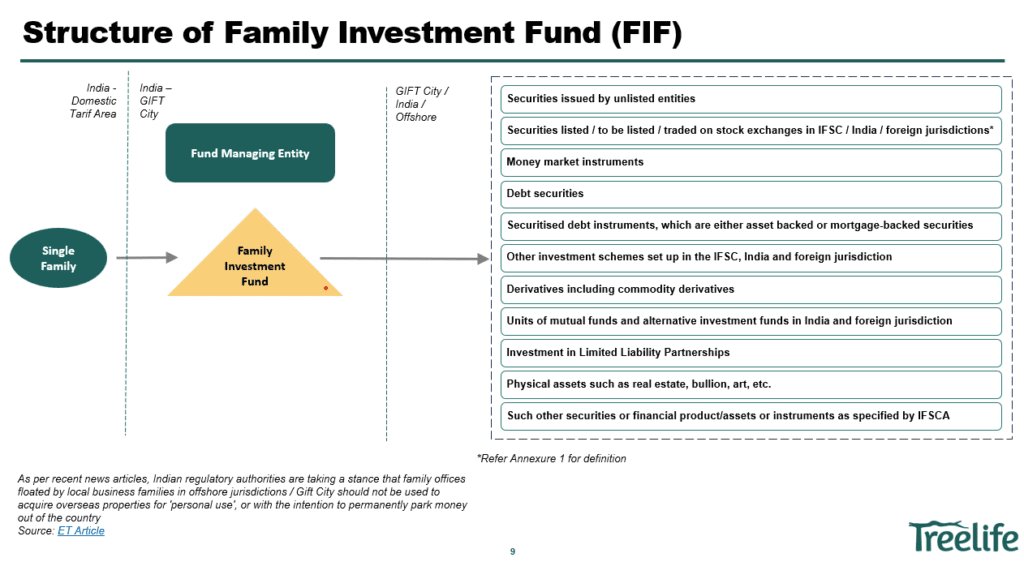
The Indian government has recently relaxed the regulations for family offices in the International Financial Service Centre (IFSC), making it an attractive option for wealthy families looking to manage their wealth and invest globally. Family offices in IFSC can set up a Family Investment Fund (FIF), which is a self-managed fund that can pool money from a single family and invest in a variety of assets, including equities, debt, and real estate. However, before getting into the benefits and details, it is important to understand what is a Family Office and What is IFSC
What is a Family Office?
A family office is a privately held company that handles investment management and wealth management for a wealthy family with the goal being to effectively grow and transfer wealth across generations.
Family offices can be either single-family offices or multi-family offices. A single-family office is owned and operated by a single family, while a multi-family office is owned and operated by multiple families.
What is International Financial Service Centre (IFSC)?
An International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) is a special economic zone that is designed to attract foreign investment in financial services. An International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) caters to customers outside the jurisdiction of domestic economy. Such centres deal with the flow of finance, financial products and services across the borders. The IFSC offers a wide range of financial services, including Banking, Insurance, Asset management, Commodity trading, Derivatives trading, Foreign exchange trading, Stock broking.
IFSC typically offer a number of benefits to financial institutions, such as:
- Favourable Tax Regime
- Liberal Regulatory Environment
- Strong Infrastructure
- Skilled Workforce
An IFSC as envisaged under the Indian context “is a jurisdiction that provides financial services to non-residents and residents (institutions) in any currency other than Indian Rupee (INR)”
An IFSC is set up to undertake financial services transactions that are currently carried on outside India by overseas financial institutions and overseas branches/ subsidiaries of Indian financial institutions.
Residential Status of Units in IFSC
- Under Foreign Exchange Management regulations (FEMA) – Treated as Non-Resident
- Under Income tax laws – Treated as Resident
IFSC in India
The first IFSC in India is the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City), which is located in Gandhinagar, Gujarat. GIFT City was established in 2015 and it is currently home to over 100 financial institutions.
In India, an IFSC is approved and regulated by the Government of India under the Special Economic Zones Act, 2005. Government of India has approved GIFT City as a Multi Services Special Economic Zone (‘GIFT SEZ’) and has also notified this zone as India’s IFSC. The launch of the IFSC at GIFT City is the first step towards bringing financial services transactions relatable to India, back to Indian shores
Family Offices in India and Family Investment Funds
India’s financial wealth is projected to reach USD $5.5 trillion by 2025, at a growth rate of 10% annually. India is also witnessing a surge in US-dollar millionaires, expected to double by 20262. As a result, there is a growing need for family offices.
The IFSCA has provided formal recognition to family offices through the IFSCA (Fund Management) Regulations, 2025, encouraging Indian family offices to establish FIFs in GIFT City to compete globally with hubs like Singapore and Dubai.
As per FM Regulations, FIF and Single family is defined as follows:
| Terms | Description |
| Family Investment Fund | A self-managed fund pooling money only from a single family and has been set up in terms of International Financial Services Centre Authority (Fund Management) Regulations, 2025 |
| Single Family | A group of individuals who are the lineal descendants of a common ancestor and includes their spouses (including widows and widowers, whether remarried or not) and children (including stepchildren, adopted children, ex nuptial children); Single family shall also include entities such as sole proprietorship firm, partnership firm, company, LLP, trust or a body corporate, in which an individual or a group of individuals of a single family exercises control and directly or indirectly hold substantial economic interest “substantial economic interest” shall mean at least 90% economic interest, as demonstrated by FIF in an appropriate manner to the satisfaction of IFSCA which may, inter alia, include: – % of shareholding in case of a company with share capital; or right to exercise control in case of a company without share capital; – % share of profits in case of partnership firm and LLP; – % of beneficial interest specified in trust deed in case of a determinate trust; or pro-rata share in the trust property in case of an indeterminate trust; or – any other manner as may be demonstrated to the satisfaction of IFSCA |

Key Aspects of an FIF
| Terms | Particulars |
| Registration | FIF to be registered with IFSCA as an Authorized Fund Management Entity (FME) |
| Possible Form | FIF can be incorporated in any of the following forms : – Company or – Trust* or – LLP * In case of a trust, the following needs to be kept in mind: (a) beneficiaries should be identifiable in the Trust deed (though not specifically named) (b) each beneficiary’s share should be capable of being determined based on the provision/formula mentioned in the trust deed (should not be at the discretion of the trustee) (c) any addition of further contributors to the Trust in addition to the initial contributors, shall not make the existing beneficiaries unknown or their shares indeterminate. |
| Minimum Corpus | Minimum corpus requirement is USD 10 million to be met and maintained within 3 years from registration |
| Tenure | The tenure of the FIF can be open ended or close ended depending on family requirements |
| Investment Limits | For Resident Individuals -To invest under LRS which is capped at USD 250,000 per person per financial year. For Indian Entity – 50% of the net worth |
| Undertaking to PO | Before the FIF commences investment activities, all individuals of a single family who contribute to the FIF directly or indirectly, shall give an undertaking to the Principal Officer, to the effect that they understand the risks, costs and benefits of investing in the FIF and that the usual investor protection measures such as disclosures, regulatory inspection and supervision, etc., may not be available to the same extent to the FIF as they are to other schemes in IFSC. |
| Borrowing | FIF may borrow funds or engage in leveraging activities as per their risk management policy |
| Setting up additional invesmtent vehicles | FIF may set-up additional investment vehicles (company / LLP / Trust / other form as specified by IFSCA) subject to prior approval of IFSCA and payment of fee as applicable to a FIF. Such additional vehicles shall also be considered as part of the FIF for the purpose of meeting the requirements specified in the regulations |
Tax and Exchange Control Regulations
| Terms | Particulars |
| Taxation of Income | 100% exemption of Business income for 10 consecutive years out of 15 years Capital gain on investments can be characterized as business profits, subjective |
| MAT/AMT | Where FIF set up as a company – No MAT Where FIF set up as an LLP – AMT of ~10.48% (including surcharge and cess) |
| TCS | TCS provisions should not apply to OPI remittances (other than LRS) |
| Amount of Investment | For individuals – LRS limits of USD 250,000 per annum For unlisted company / LLP / firms – Can invest upto 50% of networth under OPI (Refer Annexure 3 for more details) |
Pre-Requisites for FIF Application
1. Principal officer (PO)
- The applicant shall designate a principal officer who shall be responsible for overall activities of the FME including but not limited to fund management, risk management and compliance.
- PO to be based out of IFSC
- PO to meet following experience:
- A professional qualification or post-graduate degree or post graduate diploma (minimum 1 year in duration) in finance, law, accountancy, business management, commerce, economics, capital market, banking, insurance or actuarial science from a university or an institution recognised by Government or a recognised foreign university or institution or association or a CFA or a FRM from Global Association of Risk Professionals; and
- An experience of at least 5 years in related activities in the securities market or financial products including in a portfolio manager, fund manager, investment advisor, broker dealer, investment banker, wealth manager, research analyst, credit rating agency, market infrastructure institution, financial sector regulator or consultancy experience in areas related to fund management, such as deal due diligence, transaction advisory or similar activities (consultancy experience will be considered for a maximum period of 2 years and experience in other areas shall be required for at least 3 years).
- Any changes to PO to be intimated to IFSCA
2. Other Personnel FIF is required to appoint other personnel commensurate to the size of its operations and activities.
3. Fit and Proper The Applicant, PO, directors/ partners/ designated partners, key managerial personnel and controlling shareholders shall be fit and proper persons, at all times. A person shall be deemed to be a fit and proper person if :-
- such person has a record of fairness and integrity, including but not limited to-
- financial integrity;
- good reputation and character; and
- honesty
- such person has not incurred any of the following disqualifications –
- the person has been convicted by a court for any offence involving moral turpitude or any economic offence or any offence against securities laws;
- a recovery proceeding has been initiated against the person by a financial regulatory authority and is pending;
- an order for winding up has been passed against the person for malfeasance;
- the person has been declared insolvent and not discharged;
- an order, restraining, prohibiting or debarring the person from accessing or dealing in financial products or financial services, has been passed by any regulatory authority, and a period of three years from the date of the expiry of the period specified in the order has not elapsed;
- any other order against the person, which has a bearing on the securities market, has been passed by the Authority or any other regulatory authority, and a period of three years from the date of the order has not elapsed;
- the person has been found to be of unsound mind by a court of competent jurisdiction and the finding is in force;
- the person is financially not sound or has been categorized as a wilful defaulter;
- the person has been declared a fugitive economic offender; or
- any other disqualification as may be specified by the Authority.
4. Infrastructure
- FIF should have necessary infrastructure like adequate office space, equipment, communication facilities and manpower to effectively discharge its activities
- The infrastructure requirements should be commensurate to the size of its operations in IFSC
- The office should be dedicated, secured and accessible only by authorised persons of the FIF
5. Period of Validity The certificate of registration of FIF would remain valid for such period as may be specified by IFSCA unless it is suspended or cancelled by IFSCA or surrendered by FIF and taken on record by IFSCA
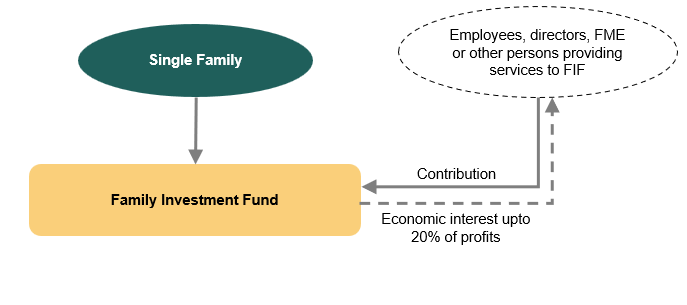
Sharing Economic Interest with Stakeholders
- An FIF cannot seek money from individuals / entities outside of the single family. However, FIF may share economic interest with its employees, directors, FME or other persons providing services to the FIF, as per its internal policy to reward the persons providing services to the FIF or to align the interest of such persons with those of the FIF.
- The FIF may accept contributions from the aforementioned persons for the limited purpose of granting economic interest to them, which in no case shall exceed an aggregate of 20% of FIF’s profits. Also, such external persons should be informed of the risks of investment in the FIF.

Exit for stakeholders with Economic Interest
- Exit may be offered by any person / group of persons from the single family who already holds interest in FIF
- Price for acquisition should not be less than the price determined by an independent third-party service provider such as a fund administrator or custodian registered with the IFSCA, a valuer registered with IBBI or such other person as may be specified by IFSCA.
- Such service provider shall take into account the following factors:
- highest price paid by any person for acquiring any interest in FIF during the last 12 months;
- the fair price of the FIF, to be determined after taking into account valuation parameters including return on net worth, book value, earning per share, price earning multiple vis-à-vis the industry average, and such other parameters as are customary for valuation of such entities.
- Service provider shall also provide a valuation report giving justification for such valuation.
Treelife experts are here to assist you. If you have any questions, please feel free to reach out to us at gift@treelife.in









